Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- L-glutamine is a conditionally essential amino acid, vital for brain function, as it serves as a precursor to neurotransmitters glutamate and GABA.
- Glutamine plays multiple essential roles in the body, including protein synthesis, muscle growth, immune system function, neurotransmitter synthesis, and glucose metabolism.
- L-glutamine supplementation can positively impact human growth hormone levels, muscle recovery, and intestinal permeability in inflammatory bowel disease.
- Maintaining a balance between glutamine and glutamate/GABA is crucial for optimal brain health, as disruptions can lead to various brain conditions and neurodegenerative diseases.
- L-glutamine supplementation can improve concentration, focus, memory, mood, and overall brain performance.
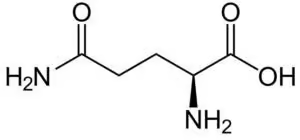
L-glutamine is a conditionally essential amino acid and main precursor for the production of the neurotransmitters glutamate and GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid) in your brain.
Glutamine is the most abundant amino acid in your body. And is involved in many of your bodily functions. Including much of the activity in your brain.[i] But L-glutamate is the most abundant amino acid in your brain. And the balance of these two is critical for optimal brain function.
The function of the glutamine/glutamate cycle is involved in protein synthesis, precursors for muscle growth, regulation of the acid-base balance in your kidneys, provides oxidative fuel for your intestine and immune system cells, provides nitrogen transport between organs, acts as precursors to neurotransmitter synthesis, nucleotide and nucleic acid synthesis for glutathione production, and glucose metabolism.[ii]
L-glutamine supplementation is mostly talked about in athletic and body building circles for its effect on human growth hormone and muscle recovery after a workout, or for its effects on inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) for its reduction in intestinal permeability. But L-glutamine is largely ignored by the nootropics community.
L-glutamine is so critically important to the optimized brain that by reading this post, you’ll understand why it may be an important addition to your nootropic stack.
L-glutamine helps:
- Neurotransmitters. L-glutamine is a precursor to the excitatory amino acid and neurotransmitter glutamate and aspartate. And the inhibitory amino acid and neurotransmitter GABA. Affecting alertness, concentration, focus, memory and mood.
- Brain Inflammation. L-glutamine helps boost your body’s immune response. Increasing antibodies to fight against viruses and bad bacteria. L-glutamine helps tame inflammatory cytokines. And L-glutamine detoxes the brain from excess ammonia and converts it into other amino acids, sugars and urea.
- Stress. L-glutamine supplies energy to immune and intestinal cells. Not enough glutamine and these cells become sluggish and can’t function properly. Supplementary L-glutamine is especially important during times of stress, tension and physical strain.
Overview
L-glutamine is an essential amino acid and precursor for the production of glutamate. Glutamate is the most abundant neurotransmitter in your brain.
As an ‘excitatory’ neurotransmitter, glutamate is released from pre-synaptic cells and then binds to post-synaptic cells inducing activation. Too much glutamate and neurons become overactive causing a toxic environment that is harmful to neurons. And to cognition.
To keep this process in check, glutamate is also a precursor to the ‘inhibitory’ neurotransmitter GABA. GABA works by preventing neural signaling in over-excited neurons caused by glutamate that could result in anxiety and depression.[iii]
The balance of glutamine and glutamate has been identified in an array of brain conditions (i.e. mental illness, tumor, neurodegeneration) as well as in normal brain function.[iv]
The precursor relationship between glutamine and glutamate/GABA is often referred to in scientific and research circles as the Gln/Gly(GABA) cycle.[v] Glutamine is naturally synthesized from glutamate and ammonia in brain cells called astrocytes in a reaction catalyzed by glutamine synthetase (GS).
Newly synthesized glutamine is transferred to neurons and hydrolyzed by phosphate-activated glutaminase (PAG) to then produce glutamate. A portion of which may be decarboxylated to GABA or transaminated to Aspartate.
Glutamate, the excitatory neurotransmitter and GABA, the calming neurotransmitter rely on this cycle to maintain homeostasis within your brain. Glutamine also modulates the synthesis of Nitric Oxide by controlling the supply of its precursor arginine.
When this cycle gets out of whack, things start to break down. The results can be particularly nasty. And result in conditions like epilepsy, or hepatic encephalopathy which effects behavior, mood, speech, sleep and the way you move.
L-glutamine becomes a “conditionally” essential amino acid when your body can’t produce enough on its own. And you need to replenish L-glutamine levels either through supplementation or food.[vi]
L-glutamine can be found in foods such as beef, pork, fish, eggs, milk and dairy products, wheat, cabbage, beets, beans, spinach and parsley.
How does L-Glutamine work in the Brain?
L-glutamine helps brain health and function in several ways. But two in particular stand out.
- L-glutamine is critical for an optimized brain. L-glutamine is a precursor to the neurotransmitter glutamate in your brain. The balance of glutamine and glutamate is crucial to an optimized and healthy brain.The normal cycling of glutamine and glutamate takes a huge amount of energy in the brain. Research has estimated that the Gln/Gly(GABA) cycle accounts for more than 80% of cerebral glucose consumption.[vii] So when you’re using nootropics like Resveratrol or PQQ to boost mental energy, much of that energy is going towards maintaining this Gln/Gly(GABA) cycle.A disruption of this cycle results in all kinds of problems including Reye’s Syndrome, epilepsy, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, anxiety, depression, and alcohol addiction.[viii]One Korean study measured Glutamate and Glutamine concentrations in the prefrontal cortex of mice infused with an astrocyte toxin. And they used other inhibitors to disrupt the Glu/Gln cycle.Glutamate and glutamine levels decreased on the 5th day in the mice. The animals experienced immobility and a decreased preference for sucrose (sugar). A sure indication in mice of depression.
Direct infusion of L-glutamine completely reversed all the impairments that were originally induced in the animals. And the researchers concluded that neuronal deficiency of L-glutamine causes depression.[ix]
- L-glutamine also helps prevent brain aging. Researchers have long been on the hunt to determine what causes the human brain to age. Recently, mitochondrial dysfunction has been implicated in the loss of brain function in neurodegenerative diseases and aging.[x] Leading to an abnormal increase in the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate.A study at the New York University School of Medicine used 28 patients with mild traumatic brain injury and 22 matched controls. Gray and white matter in their brains was measured using MRI’s.The study found that one year after traumatic brain injury there was significant global brain atrophy. Much larger than in the control subjects.The team noted the amount of brain damage from just one concussion. And that this type of injury was not exclusive to a severe blow to the head. Even mild injury could cause brain damage.[xi] Most of the damage was associated with a disrupted Glu/Gln cycle and an abnormal increase in glutamate levels.[xii]
How things go bad
Low levels of L-glutamine are associated with a variety of health problems.
↓ Cellular energy drops and immune system weakens
↓ Short- and long-term memory declines
↓ Mood and anxiety disorders, insomnia, and lack of concentration
↑ Muscle spasms, hypertension, convulsion, Tourette’s Syndrome and epilepsy
↑ Ammonia levels rise in brain cells[xiii]
↓ Poor digestion, bloating, flatulence, and constipation
When your neurotransmitters, including L-glutamine and glutamate are in balance, you feel motivated, productive and energetic. And you feel calm and relaxed during downtime.
When L-glutamine levels are low you feel filled with dread, you’re constantly worried, you have racing thoughts, and you’re frequently late and disorganized.
Many people in this L-glutamine -slump resort to high carbohydrate foods, and drugs or alcohol to relax.
L-Glutamine benefits
The amino acid L-glutamine is the precursor to L-glutamate production in your body. L-glutamate gets converted to GABA.
 Glutamate is your body’s most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter. Which is responsible for attention span, brain energy, learning ability, memory, and staying awake.
Glutamate is your body’s most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter. Which is responsible for attention span, brain energy, learning ability, memory, and staying awake.
An enzyme called glutamate decarboxylase converts glutamate to GABA. It does it with the help of the active form of Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxal-5-Phosphate (P5P)).
The amino acid taurine helps increase the communication and productivity of this enzyme. And zinc helps the release of GABA from its receptors.
When this Gln/Gly(GABA) cycle works efficiently, you feel relaxed with no stress or feelings of anxiety. Detoxification of your liver results in a more restful night’s sleep. Focus, concentration, memory and mood all improve.
How does L-Glutamine feel?
During times of chronic, long-term stress caused by physical exertion or illness, glutamine levels in your body can drop by 50% or more.[xiv]
Supplementing with L-glutamine can improve your quality of life, increase energy levels, reduce muscle aches, improve digestion and gut health, improve quality of sleep, and reduce pain and fatigue.
When you balance L-glutamine levels in your brain, you feel relaxed and calm. Cravings for sugar and alcohol will decline.
L-glutamine will help in recovery from workouts and improve performance. You may find it easier to lose weight.
Many neurohackers use L-glutamine to help heal Leaky Gut Syndrome and reduce the symptoms of Crohn’s and Celiac Disease.
As a nootropic, L-glutamine can help improve alertness, concentration, focus, memory and mood.
L-Glutamine Clinical Research
L-glutamine was identified as a neurotransmitter several decades ago. And there has been a lot of research on L-glutamine published since. But most of it is focused on strength training and maintaining muscle mass in athletes. And for people healing from surgery or recovering from illness.
But L-glutamine can be a powerful nootropic as well. Here are a couple of studies looking at L-glutamine for brain health.
L-glutamine Increases Human Growth Hormone
Bodybuilders and athletes use supplementary L-glutamine to help repair and build muscle. And there are several studies supporting the notion that L-glutamine increases Human Growth Hormone.
In one study, researchers worked with 9 healthy subjects and gave them 2 grams of L-glutamine in a cola drink. Blood samples were taken before drinking the cola-spiked drink, then again at 30 mins., 60 and 90 mins.
The researchers found that both blood L-glutamine and human growth hormone levels were significantly higher than before taking L-glutamine. The team concluded that “a surprisingly small oral L-glutamine load was capable of elevating growth hormone”.[xv]
Human growth hormone and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) are intricately linked. BDNF is involved in Long-Term Potentiation and the encoding of long-term memories.
L-glutamine Improves Cerebral Performance
Lack of concentration and poor memory can be improved by supplementing with L-glutamine with Vitamin B3 (niacin). Some of the glutamine in your blood is transformed into glutamic acid in your brain.
Glutamic acid functions first as fuel, but it also gets rid of excess ammonia by binding to this cellular toxin and converting it into glutamine.
A study in the Netherlands conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled trial with 42 healthy men and woman aged 40 – 76 years. Subjects received a 5-gram stack containing glycine, L-glutamine and niacin twice daily for 3 weeks.
The L-glutamine stack increased Human Growth Hormone a whopping 70% compared to placebo. But surprisingly it wasn’t the growth hormone that improved memory and vigor. It was insulin-like growth factor-I that improved memory and vigor. Attributed to the L-Glutamine stack the subjects took for 3 weeks.[xvi]
L-Glutamine Nootropic Recommended Dosage 
Most people don’t get enough L-glutamine from food alone. And why adding L-glutamine to your nootropic stack can boost your immune system, improve your ability to fight infection and diseases, and boost cognition.
The recommended daily dosage of L-glutamine is 2 to 5 grams per day.
Serious power athletes often dose up to 10 grams of L-glutamine per day.
L-Glutamine Side Effects
L-glutamine is considered very safe when taken in normal recommended doses.
Rarely do people report side effects like nausea, vomiting, flatulence, abdominal pain, constipation, dry mouth, hemorrhoids, dizziness, depression, skin rashes, insomnia and increased sweating. Remember, the balance between L-glutamine and glutamate (Gln/Gly(GABA) cycle) is critical for optimal health.
If you are dealing with any form of cancer and are either being treated for it or are in remission, you should consult with your doctor before you start supplementing with L-glutamine.
If you are dealing with cirrhosis of the liver, you should avoid L-glutamine. If you have severe liver disease that includes difficulty thinking or confusion (hepatic encephalopathy), don’t use L-glutamine.
If you are allergic or sensitive to Monosodium Glutamate (MSG), you may be sensitive to L-glutamine because your body converts it to glutamate.
And if you have a severe mental disorder including mania or frequently have seizures you may want to avoid L-glutamine.
Types of L-Glutamine to Buy
L-glutamine as a supplement is available in tablet, capsule and powder.
The most commonly available form of L-glutamine as a nootropic supplement is called “free form” glutamine.
Trans-Alanyl or Alanyl-L-glutamine is an amino acid attached to another amino acid which aids in digestion of this supplement.
If you are using it to boost athletic performance and speed recovery, both forms of L-glutamine are best taken right before or after a workout. Using it with small meals before or after your workout session can help support your metabolism and weight loss goals. And will assist in muscle building, recovery and maintenance.
Nootropics Expert Recommendation
L-Glutamine 2 – 5 grams per day.
 I recommend using L-glutamine as a nootropic supplement if you’re dealing with anxiety or stress. And to calm or keep in check some of the stimulatory effects of some nootropics.
I recommend using L-glutamine as a nootropic supplement if you’re dealing with anxiety or stress. And to calm or keep in check some of the stimulatory effects of some nootropics.
Your body does make L-glutamine on its own from glutamate in your brain. But most people do not maintain an adequate supply of L-glutamine in their system.
And if you’re dealing with illness, recovery from surgery, strenuous physical activity like working out, Leaky Gut Syndrome, Crohn’s or Celiac Disease, and need some help in recovery, L-glutamine can help.
L-glutamine also helps to curb the desire for sugar, carbs and alcohol.
We suggest trying a L-glutamine supplement first at a dose of 500 mg. And see how you react. You can safely dose up to 20 grams of L-glutamine per day. But most neurohackers find much lower doses effective for boosting cognition, mood and memory.







Join The Discussion - 138 comments
alex
May 28, 2024
L-glutamine should be taken morning or night?
David Tomen
May 31, 2024
Alex, entirely up to you. L-Glutamine goes on to produce glutamate which goes on to produce GABA which goes on to produce Human Growth Hormone. So you’ll get the most benefit from this supplement by using it during the day.
Jack
May 11, 2024
Hello David,
I’ve tried taking L-glutamine to help with my intestines. I suspect they may be leaky.
However, taking just 1g of it caused insomnia for me. So, I took a break and tried again. But each time, it leads to insomnia.
Alongside this, I have generalized anxiety disorder.
Could the fact that L-glutamine causes insomnia for me potentially indicate that I already have a high level of glutamate? Or is this unrelated?
As I’ve been searching for years for ways to treat my generalized anxiety disorder without success, I wondered if reducing glutamate could be helpful? If so, how should I proceed?
Thank you in advance for your help,
Jack
David Tomen
May 12, 2024
Jack, glutamine goes on the produce glutamate which then produces GABA and then Human Growth Hormone. Noopept prevents the release of excess glutamate in your brain.
Jack
May 15, 2024
So if I understand correctly, Noopept can reduce the amount of glutamate in the brain, but will it also reduce the amount of GABA given that glutamate is converted into GABA? Or will it instead speed up the conversion?
David Tomen
June 11, 2024
Jack, Noopept elevates concentrations of cycloprolylglycine (CPG) in the brain. CPG is a dipeptide consisting of proline and glycine which acts as a modulator of acetylcholine transmission and AMPA receptor function. it does not “reduce” glutamate. But it modulates the way glutamate works which prevents glutamate toxicity. It does not negatively affect GABA production or function.