Table of Contents
Caffeine (1,3,7-trimethylxanthine) is the most widely used psychoactive drug in the world. And is considered a nootropic because used in moderation it helps improve reaction time, alertness, memory and mood.
 A Penn State University study in 2014 found 85% of the US population consumes at least one caffeinated beverage per day.[i]
A Penn State University study in 2014 found 85% of the US population consumes at least one caffeinated beverage per day.[i]
Coffee typically contains more caffeine than most other beverages. But caffeine is also found in carbonated soda, tea, energy drinks, energy shots, some fruit or fruit-flavored drinks and a few pre-formulated nootropic stacks.
Caffeine consumption provides a boost in mental alertness, concentration, better athletic performance, and less physical and mental fatigue.
Caffeine and coffee consumption has also been associated with weight loss, improved glucose tolerance, a lower risk of Type II diabetes, reduced risk of Parkinson’s Disease and fewer Parkinson’s symptoms, and reduced risk of several types of cancer.
In this review we are focusing on caffeine benefits to cognitive health.
Caffeine helps:
- Neurotransmitters. Caffeine is an adenosine antagonist which influences acetylcholine, epinephrine (adrenaline), serotonin and boosts the use of dopamine. Providing the stimulant effect experienced when consuming caffeine.[ii]
- Neuroprotectant. Caffeine provides a protective effect by boosting gene expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Studies show chronic caffeine consumption may protect against developing neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.[iii]
- Mood. Caffeine improves mood within an hour of consumption.[iv] Because it increases the density of GABA receptors, potentiates dopamine, and causes some serotonin receptors to be more responsive.
Overview
Caffeine (1,3,7-trimethylxanthine) is the most widely consumed stimulant and psychoactive drug on the planet.
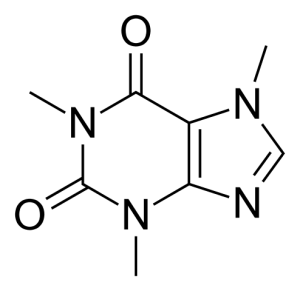
Caffeine is a methylated xanthine which are a group of alkaloids commonly used as mild stimulants. Xanthine is a purine base naturally found in most of your body’s tissues.
Caffeine is chemically related to adenine and guanine which are bases of DNA and RNA.
The most common source of caffeine is the coffee bean from which coffee is extracted. Other natural sources include leaves of the tea plant, cocoa beans, kola nuts, holly leaves, yerba mate leaves, seeds from guarana berries, and guayusa leaves.
The earliest evidence of coffee as a beverage comes from 15th century Sufi monasteries in Yemen. By the 16th century coffee made its way north through the Middle East to Italy and the rest of Europe.
Coffea plants where then exported with early explorers and settlers in the Americas.
Chinese legend tells us tea as a source of caffeine was first used in about 3,000 BCE.
The earliest evidence of caffeine use native to the Americas comes from cocoa bean residue found in a Mayan pot dating from 600 BCE.
Today, coffee and tea are drunk in most countries. But typically, one predominates. For example, coffee is the preferred caffeine source in Europe and the Americans. While tea is preferred elsewhere.[v]
Despite the world-wide popularity of caffeine use as a stimulant by everyone from students to the military to seniors – the only organization that currently bans the use of caffeine is the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA).[vi]
How does Caffeine work in the brain?
Caffeine boosts brain health in several ways. But two in particular stand out.
- Caffeine promotes alertness. Caffeine is an adenosine receptor antagonist. Adenosine functions as an inhibitory neurotransmitter in your brain. During the day, as adenosine levels rise, wakefulness decreases and eventually leads to sleep.As an adenosine antagonist, caffeine acts by blocking two of four adenosine receptor subtypes A1 and A2A. Preventing adenosine from coupling with these two receptor subtypes increases wakefulness.[vii]A 13-night sleep lab study was conducted with 18 ‘normal’ young adult males. Each participant received a cup of warm water, 1-, 2- or 4-cups of regular coffee, a 4-cup equivalent of decaffeinated coffee, or a 4-cup equivalent of caffeine.
Regular coffee produced dose-related changes in standard EEG sleep parameters. And 4-cups of coffee acted the same as the equivalent dose of caffeine.
Caffeine caused REM sleep to shift to the early part of the night and stage 3 and 4 sleep to shift to the later than in a normal sleep cycle.
The researchers concluded that coffee and caffeine may be used in normal people to induce symptoms of insomnia.[viii]
- Caffeine improves physical endurance. Multiple studies show that trained athletes experience improved performance from low to moderate doses of caffeine.
Some studies found improved trial performance, and maximum cycling power. Likely from a greater reliance on fat metabolism and decreased muscle fatigue.
Caffeine helps athletes train longer and at greater power output. And post-exercise recovery benefits from more glucose being taken up by cells and stored as glycogen.
In fact, caffeine can be so effective in sports that the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) banned the use of caffeine in athletes from 1962 – 1972 and again from 1984 – 2003.
Caffeine was removed from the prohibited list of drugs but is still part of WADA’s monitoring program to monitor the possible misuse of it in sport.[ix]
How things go bad
 In 1994, scientists confirmed for the first time that caffeine is addictive. In the same way you can become addicted to cigarettes, alcohol or drugs.[x]
In 1994, scientists confirmed for the first time that caffeine is addictive. In the same way you can become addicted to cigarettes, alcohol or drugs.[x]
In May 2013 caffeine withdrawal was included as an official mental disorder in the 5th edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM).[xi]
Caffeine affects your body for about 4 hours after it is consumed. Withdrawal symptoms set in 12 – 20 hours after your last dose. The worst symptoms set in after about 2 days and can last for up to a week.
↑ Drowsiness increases
↑ Mood swings increase
↑ Headaches increase
↓ Alertness decreases
Consuming caffeine increases dopamine in your brain which improves mood. Once caffeine leaves your system, you can get grumpy and tired.
Researchers found continuous caffeine consumption increases your number of adenosine[xii], dopamine[xiii], and acetylcholine receptors[xiv]. And is likely why long-term use of caffeine causes tolerance.
Caffeine benefits
Caffeine is the most widely used psychoactive drug in the world. Boosting attention and normalizing mood and cognition.
 A study at John Hopkins University showed that caffeine enhances consolidation of long-term memory. This enhanced memory performance occurred 24-hours after caffeine consumption.[xv]
A study at John Hopkins University showed that caffeine enhances consolidation of long-term memory. This enhanced memory performance occurred 24-hours after caffeine consumption.[xv]
This study is especially relevant if you are looking for nootropics for study. Because it means caffeine consumed after a study session helps consolidate memory of what you studied.
Caffeine improves reaction time. And increases alertness and focus.[xvi]
Coffee and caffeine have been shown to repair DNA damage.[xvii]
Long-term caffeine use has been associated with reduced risk of diabetes.[xviii]
Increased caffeine intake is associated with decreased risk of malignant melanoma.[xix]
Increased caffeine consumption also protects against cataract blindness.[xx]
How does Caffeine feel?
How you feel on caffeine varies from person to person. But for most it depends on how much you consume.
Caffeine acts as a central nervous system stimulant. Once it crosses the blood-brain barrier the most noticeable effect is alertness.
Caffeine stimulates the release of dopamine. Which accounts for the pleasant feeling you associate with your first morning coffee.
Most neurohackers find consuming caffeine makes you more productive. You should find it easier to concentrate and get things done.
Using a caffeinated beverage after a study session should help you recall what you studied more easily.
But caffeine later in the afternoon or evening resets your internal body clock (circadian rhythm) and delays the natural rise of melatonin. Your brain’s primary sleep hormone.
So consuming coffee, tea or an energy drink too late in the day will likely leave you unable to sleep.
And quitting caffeine abruptly can lead to some nasty withdrawal symptoms. See the “Side Effects” section of this review for more.
Caffeine Clinical Research
Caffeine Reduces Risk of Suicide
Drinking several cups of coffee daily appears to reduce the risk of suicide by about 50% according to a study at the Harvard School of Public Health.
Study authors reviewed data from 3 large studies and found that risk of adult suicide who drank 2 – 4 cups of caffeinated coffee per day was about half compared to those who drank decaffeinated coffee or no coffee.
Caffeine not only stimulates the central nervous system but also acts as a mild antidepressant by boosting production of serotonin, dopamine and epinephrine.
After analyzing all the data, researchers concluded, “our results suggest an association between greater consumption of coffee and a lowered risk of suicide”.[xxi]
Caffeine Improves Cognitive Performance
68 U.S. Navy Seal trainees were randomly assigned either 100, 200, or 300 mg of caffeine or placebo in capsule form after 72 hours of sleep deprivation and continuous exposure to other stressors.
Cognitive tests included visual vigilance, reaction time, working memory, and mood.
The chief researcher of the study, Harris Lieberman reported, “Even in the most adverse circumstances, moderate doses of caffeine can improve cognitive function, including vigilance, learning, memory, and mood state.
When cognitive performance is critical and must be maintained during exposure to severe stress, administration of caffeine may provide a significant advantage. A dose of 200 mg appears to be optimal under such conditions.”
Caffeine Reduces Depression
Recent clinical studies have shown that caffeine intake enhances the effect of antidepressants in rodents.
To find out if it worked in humans, researchers in China recruited 95 male inpatients currently on antidepressant medication. Patients were given 60 or 100 mg of caffeine daily or a placebo daily for 4 weeks.
The results showed low dose caffeine improved cognitive performance in depressed patients.
And the researchers concluded caffeine helps reverse the development of depression. And “enhances the outcome of antidepressant treatment in major depressive disorder”.[xxii]
Caffeine Boosts Memory
60 undergraduate students at the University of Arizona were given an 8-counce cup of Starbucks Italian Bold coffee with caffeine or decaffeinated (as the placebo) between 6 – 7 am.
The participants were then instructed to read a book for 30 minutes.
Students who drank the caffeinated coffee performed significantly better than placebo with 30% improvement in memory.
The researchers performed the same test with 43 students between 2 – 4 in the afternoon. In contrast to the morning session, the students did not experience any memory benefit.
The study authors concluded that “caffeine has a specific benefit for memory during students’ non-optimal time of day – early morning. These findings have real-world implications for students taking morning exams.”[xxiii]
Studies show that older adults also have better memory in the morning. But memory ability declines in the afternoon.
In another study adults over 65 who considered themselves “morning-types” were tested twice over an interval of 5 – 11 days. Once in the morning and once in the late afternoon.
Adults who ingested decaffeinated coffee showed a significant decline in memory performance from morning to afternoon.
In contrast, those who ingested caffeine showed no decline in performance from morning to afternoon.
The conclusion is obvious; older adults perform better in the afternoon when it comes to memory by consuming a caffeinated beverage.[xxiv]
Caffeine Recommended Dosage
According to the Mayo Clinic, 400 mg of caffeine per day appears to be safe for most healthy adults. About the amount of caffeine in four cups of regular brewed coffee.[xxv] Or 1 ½ Starbucks ‘tall’ coffees.
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommend ages 12 – 18 limit caffeine intake to no more than 100 mg per day.[xxvi]
The half-life of caffeine is 4 – 6 hours and you experience the effects of caffeine for at least 4 hours.
Be aware that sources of caffeine include coffee, tea, Coke, Pepsi, Dr. Pepper, Mountain Dew, 5-Hour Energy Shot, Monster Energy Drinks.
And one Starbucks tall coffee can contain 235 mg of caffeine.
So it’s surprisingly easy to quickly exceed your personal caffeine limit before you begin to experience caffeine toxicity.
Everyone has a different tolerance level before experiencing the symptoms of a caffeine overdose. Listen to your body to know what your personal limit is.
Caffeine + L-Theanine
One of the most popular and simple nootropic stacks is caffeine stacked with L-Theanine.
 A study with 49 people was conducted at Wageningen University in the Netherlands to assess the effects of caffeine, L-Theanine and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) (which is found in green tea) on mood and cognitive performance.
A study with 49 people was conducted at Wageningen University in the Netherlands to assess the effects of caffeine, L-Theanine and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) (which is found in green tea) on mood and cognitive performance.
Study authors noted as little as 40 mg of caffeine has been shown to improve performance on long-duration cognitive tasks, alertness, arousal and vigor.
The team also noted just 200 mg of L-Theanine improved feelings of calmness, relaxation and less tension.
And when L-Theanine and caffeine were combined there was a significant improvement in alertness and attention-switching task performance. More so than with caffeine alone.
The researchers concluded, “these studies provided reliable evidence showing that L-theanine and caffeine have clear beneficial effects on sustained attention, memory, and suppression of distraction.
Moreover, L-theanine was found to lead to relaxation by reducing caffeine induced arousal”.[xxvii]
The best pre-formulated caffeine + L-Theanine stack I’ve tried, and use regularly is Click for Performance Lab® Caffeine 2 . It contains Natural Caffeine (from Coffea Robusta seeds) 50 mg, L-Theanine 100 mg, L-Tyrosine 250 mg, with a balanced NutriGenesis® B-Complex. For alert clean energy without the jitters.
Caffeine Side Effects
Caffeine is a xanthine alkaloid that can be profoundly toxic and deadly.
But reports of caffeine overdoses resulting in death are relatively rare.[xxviii] However, it’s surprisingly easy to go into caffeine toxicity territory so please always check the labels on caffeinated beverages and energy drinks.
Doses as little as 200 mg can be toxic to sensitive people.
Symptoms of caffeine toxicity include feeling ‘wired’, breathing trouble, confusion, diarrhea, fainting, fever, hallucination, increased thirst and/or urination, heart palpitation, restlessness, sweating, muscle tremors and rapid heartbeat.
Caffeine is addictive and you can quickly build up a tolerance to its energizing effects.
Caffeine withdrawal is serious and can include anxiety, fatigue, headaches, irritability, digestive problems, and trouble concentrating.
Do NOT combine any source of caffeine with ephedrine, quinolone antibiotics, propranolol, theophylline, certain birth control pills, or echinacea. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are using any other medications that may be affected by caffeine.
Doses of 10 grams of caffeine can be fatal. Although this varies from person to person.[xxix] In one case a person died from only 240 mg of caffeine.
A teaspoon of caffeine powder has 3,200 mg of caffeine.
Types of Caffeine to buy
 You get caffeine from a variety of sources including coffee, green or black tea, energy drinks or shots, caffeinated beverages like cola, yerba mate, chocolate, OTC stimulant supplements, some weight loss drugs, and a few pre-formulated nootropic stacks.
You get caffeine from a variety of sources including coffee, green or black tea, energy drinks or shots, caffeinated beverages like cola, yerba mate, chocolate, OTC stimulant supplements, some weight loss drugs, and a few pre-formulated nootropic stacks.
Caffeine is a natural alkaloid found in the seeds and leaves of certain plants. Caffeine in coffee originates primarily from the bean of Coffea arabica, a shrub or small tree that grows in high-altitude subtropical regions of the world.
Caffeine anhydrous is manufactured from the beans of coffea plants. “Anhydrous” means without water. Caffeine is extracted from the bean and dehydrated. Which produces a highly concentrated caffeine powder.
I use and recommend: Click for Performance Lab® Caffeine 2 . It contains Natural Caffeine (from Coffea Robusta seeds) 50 mg, L-Theanine 100 mg, L-Tyrosine 250 mg, with a balanced NutriGenesis® B-Vitamins.
Nootropics Expert Recommendation
I recommend using Caffeine as a nootropic supplement.
Your body does not make caffeine on its own. You get varying amounts of caffeine from coffee, tea, energy drinks and shots, yerba mate, and some pre-formulated nootropic stacks.
All caffeine is the same regardless of the source. Its effects are dose-dependent up to a tolerable limit.
Caffeine is particularly effective as a study aid because consumption of a caffeinated beverage after your study session should help you consolidate the memory of what you studied.
Caffeine is especially helpful for athletes because it improves performance and reaction time. And increases alertness and focus.
And caffeine helps improve mood.
Tolerance to caffeine builds quickly so expect to continue dosing with moderate amounts of caffeine every day to avoid withdrawal symptoms.
And caffeine is great to stack with L-Theanine because the combination helps increase alertness, memory and mood. While L-Theanine helps counteract some of the negative symptoms of caffeine’s stimulant qualities.
I use and recommend: Click for Performance Lab® Caffeine 2 . It contains Natural Caffeine (from Coffea Robusta seeds) 50 mg, L-Theanine 100 mg, L-Tyrosine 250 mg, with a balanced NutriGenesis® B-Complex.
Suggested starting dose of caffeine is 200 daily. See how your body reacts. The absolute upper limit is no more than 500 mg of caffeine per day.









Join The Discussion - 85 comments
Wong
January 19, 2025
Hi David
I would like to know I often have headache but when I take panadol, my headache goes away . So I try taking caffeine + l
Theanie and my headache was gone too.I notice that some Panadol contain caffeine but is there any scientific studies that shows caffeine helps with me headache ?
David Tomen
January 20, 2025
Wong, check the 3rd paragraph under “introduction” in this study for an explanation: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10385675/
Daniel
October 14, 2024
If adenosine receptors are blocked too often, the brain assumes that they stop working and starts to increase their number.
The more receptors → the more caffeine molecules are needed to block them and provoke the same vigor. This is one of the reasons why tolerance from coffee appears when we have to increase the dose.
David Tomen
October 15, 2024
Daniel, that makes some logical sense for caffeine tolerance. But you do you have any proof that this is a valid reason?
Yoshi
May 3, 2024
Dear David,
there is a supplement called theacrine, which is similar to caffeine.
Hope you will add it to the nootropics list. You are my go to information source!
Maybe you know if theacrine is water soluble?
Best regards,
Yoshi
David Tomen
May 8, 2024
Yoshi, I started researching Theacrine to write a review but abandoned it after a couple of days. Because I could not come up with any good science supporting its use as a nootropic.
Paraxanthine is the most active component found in caffeine: https://nootropicsexpert.com/paraxanthine/