Table of Contents
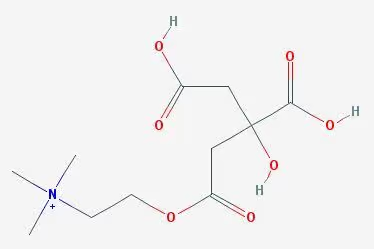
Choline Citrate is choline combined with citrate which is an ester of citric acid. Binding choline to citrate may contribute to the synthesis of acetylcholine (ACh) in your brain.
The two precursors required for acetylcholine (ACh) synthesis are Choline (2-hydroxy-N,N,N-trimethyl-ethanaminium) and the enzyme acetyl-Coenzyme A (Acetyl-CoA).
Citrate is the source of about one third of the acetyl groups used for the synthesis of ACh.[i]
Your brain uses acetylcholine to maintain clear communication. In fact, it’s used to maintain communication between all the cells in your body.
And you need choline for cognition, memory, sleep and even maintaining your balance, stability and mobility. Your brain needs choline to function.
When choline is in short supply, your brain goes on a scavenger hunt. And starts to steal choline from nerve cell membranes. In your brain’s attempt to maintain normal acetylcholine signaling, it starts taking cells apart.[ii]
This works in the short term. Your brain uses this technique to keep your memory and other functions running smoothly. But in the long run it takes a toll on your brain at the cellular level.[iii]
This is the primary reason you need to add a choline supplement to your nootropic stack.
Choline Citrate helps:
- Brain Energy. Choline Citrate improves mood, and boosts mental energy. Choline is needed to maintain alertness and clarity of thought.
- Neurotransmitters. Choline Citrate helps improve memory. Once it reaches your brain it helps produce the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.[iv]
- Brain Optimization. Choline Citrate contributes to the development of new brain cells. And enhances your brain’s ability to repair damaged cell membranes.
Overview
Choline Citrate is choline combined with citrate, an ester of citric acid. Citrate and choline may help in the synthesis of acetylcholine (ACh). The combination of these two ingredients increases the effectiveness of this source of choline above simply providing another source of choline to the brain.
Choline was declared an essential nutrient by the Food and Nutrition Board of the National Institute of Medicine (USA) in 1998.
Choline is considered an essential nutrient because when your body uses it faster than it can produce it, you need supplemental choline either from food or a supplement.
Choline is found in foods such as fish, beef steak, liver, chicken liver, eggs, cod, broccoli, peanut butter and milk.
You need choline for the production of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. And to form phosphatidylcholine (PC), a key ingredient in the membranes encasing each brain cell.
In fact, choline is so vital to cognition and nerve function that, without it, we couldn’t move, think, sleep or remember anything. Numerous human and animal studies have shown enhanced brain function when given supplemental choline.
Citrate is a citric acid ester which provides a third of the acetyl groups used in the acetylcholine (ACh) synthesis process. You can get citric acid from citrus fruit like lemons and limes.
And citrate plays another important role in the brain. Citrate is an intermediate in the Krebs cycle (also known as the TCA cycle or Tricarboxylic Acid cycle, or Citric acid cycle).
Citrate synthase catalyzes the condensation of oxaloacetate with acetyl CoA to form citrate. Citrate then acts as the substrate for aconitase and is converted in aconitic acid. This cycle ends with the regeneration of oxaloacetate.
This series of chemical reactions is the source of 2/3’s of the energy we get from food. Most of the energy made available by these steps is transferred to form NADH. Which then drives adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthesis within mitochondria and provides the energy needed for brain cells.[v]
Choline Citrate vs. Choline Bitartrate vs. CDP-Choline vs. Alpha GPC: What’s the Difference?
Choline is a water-soluble nutrient and its composition is similar to B-vitamins. Choline Citrate, CDP-Choline, Choline Bitartrate and Alpha GPC are all sources of choline.
Choline Citrate: An economical form of choline combined with citrate, and about 50% choline by weight. So 1 gram of Choline Citrate offers 500 mg of actual choline. Choline Citrate not only provides your brain with choline, but comes with one of the acetyl groups necessary for acetylcholine (ACh) synthesis.
Choline Bitartrate: An economical form of choline, and about 40% choline by weight. So 1 gram of Choline Bitartrate offers 400 mg of actual choline. It does not cross the blood-brain barrier as readily as other sources of choline. So you won’t experience the same level of nootropic benefits as with Alpha GPC or CDP-Choline.
CDP-Choline (cytidine 5′-diphosphocholine): Is only about 18% choline by weight. Your body naturally synthesizes choline into CDP-Choline (Citicoline). It’s then converted to phosphatidylcholine (PC) which is one of two fatty acids that make up the outer layer of cell membranes. And PC provides the choline needed to synthesize acetylcholine (ACh).
Alpha GPC: About 40% choline by weight and easily crosses the blood-brain barrier. Alpha GPC naturally occurs in your brain as a byproduct of phosphatidylcholine (PC). When your brain needs more choline, and the choline floating around in your brain is running low, it breaks down PC from cell membranes. And turns it into Alpha GPC.
Your body and brain loves it when you use choline. Because it doesn’t have to cannibalize its own cells to get more choline.
How does Choline Citrate work in the Brain?
Choline Citrate boosts brain health and function in several ways. But two in particular stand out.
- Choline Citrate boosts acetylcholine (ACh). Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter tied to memory and overall brain function.
Choline Citrate is a precursor to acetylcholine. Improving the efficiency of communications between neurons in your brain. This increase in neural signaling boosts memory, learning, cognitive processing and mental clarity.
But researchers found that circulating choline in the brain decreases with age. This study recruited younger adults between 20 and 40 years, and older adults between 60 and 85 years.
After fasting overnight, the subjects received 50 mg of a choline supplement per kilogram of body weight. Labs were drawn to determine choline concentration in the blood. And proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) was performed to determine the relative concentration of cytosolic choline-containing compounds in the brain.
Both tests were done before, and 3 hours after choline supplementation. Levels of choline in the blood and brain of study subjects were similar before choline supplementation.
But after choline supplementation, the younger subjects showed a 60% increase of choline in their blood and brain. The older subjects showed only a 16% increase in choline levels.
The researchers concluded circulating choline in the brain decreases with age. And given the key role of choline in brain function, this change may be a contributing factor in onset of late life neurodegeneration and dementia.[vi]
So according to this study, older adults should be supplementing with higher doses of a choline supplement like Choline Citrate to maintain cognitive function compared to younger adults.
- Choline Citrate Boosts Memory. Researchers and medical professionals have long known about poor memory in people with a choline deficiency.
A study at Northwestern University in Chicago tested people with a choline deficiency. They gave them a series of memory tests and found their scores below average.
In this study, they then gave one group extra choline, and the others were given a placebo. After 24 weeks, both groups repeated memory tests.
The group who received extra choline showed a dramatic improvement in memory. The placebo group performed poorly as expected with scores the same as on the original test.[vii]
How things go bad
As we get older, our brain chemistry and energy metabolism changes. But choline deficiency can happen at any age from infancy through to our late adult years.
↓ Brain fog and/or a sense of confusion
↓ Fatigue or lack of energy
↓ Unable to learn new things
↓ Memory loss and poor recall
↓ Feeling distracted or irritable
↓ Poor balance
↓ Lack of energy/fatigue
Our bodies are influenced by the food we eat (and what we don’t eat!), what we drink, lifestyle habits, and even the air we breathe.
Choline Citrate can help reverse cognitive decline. It can help you perform better in your work, and at school. By boosting acetylcholine and repairing neural cell membranes.
Choline Citrate benefits
Research from hundreds of studies have shown that choline will:
- Eliminate brain fog and confusion
- Boost energy
- Improve learning
- Enhance memory and recall
- Help focus and reduce irritability
- Improve physical performance
- Eliminate fatigue
Choline Citrate is water-soluble. After it’s digested it will enter your bloodstream and cross the blood-brain barrier. Once in your brain it boosts neural signal transmission, and helps repair neurons.
Choline Citrate improves your brain function and memory by increasing the production of acetylcholine. And prevents neurons from getting cannibalized when your brain is searching for more choline.
How does Choline Citrate feel?
After taking Choline Citrate you should feel a boost in your ability to think, mood should improve, and your energy level should go up.
Choline Citrate influences the level of acetylcholine in your brain. This crucial neurotransmitter affects memory, cognition, recall and learning.
Low levels of choline will leave you with brain fog and an inability to think clearly. You may also experience a drop in mood and some irritability.
If you’re using anything from the racetam-family of nootropics and you experience a headache – your brain is likely starved for choline.
Choline Citrate Clinical Research
Choline Boosts Cognition
The Framingham Heart Study is a long-term, ongoing cardiovascular study on residents in the town of Framingham, Massachusetts. The study began in 1948 with 5,209 adults. And is now on its 3rd generation of participants.
This study of Framingham Offspring involved 1,391 dementia-free subjects. Ages ranged from 36 – 83 years. The participants underwent a food-frequency questionnaire, and MRI brain scan. The study was in two parts, from 1991 to 1995, and 1998 to 2001.
Study participants were tested for verbal memory, visual memory, verbal learning and executive function. And a MRI-scan measured brain volume.
The study concluded that those residents with higher choline intake demonstrated significantly better cognitive performance.[viii]
Choline Citrate Helps with Exercise and Muscle Performance
Choline Citrate boosts mental energy, focus and concentration. All critical for physical activity and athletic performance.
Choline’s effect on your metabolism and neurotransmitters in the brain produce quicker reaction times. And shorten the time needed for mental processing.
Choline helps improve your energy levels, mood, and recovery time following a workout. It is also critical for muscle nerve function, and in preventing fatigue, muscle aches and pain following a workout.
When your muscles move, choline is needed to activate the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh). ACh elevates muscle enzymes, and muscle integrity.[ix]
Researchers found that providing 2 grams of choline prior to exercise prevented a fall in choline levels. And raised choline levels above baseline values for up to 2 hours after exercise.
The researchers found that choline citrate and choline bitartrate were equally effective. One randomized, placebo-controlled study found improvements in running times by a significant amount over a 20-mile course when compared to those using a placebo.[x]
Choline Citrate Recommended Dosage
Recommended Choline Citrate dosage is 500 mg to 3,000 mg per day.
You can use higher doses of Choline Citrate because this is a water-soluble version of choline. And a limited amount of this choline source will cross the blood-brain barrier.
Studies have found that age has a significant effect on choline uptake into the brain. So older neurohackers are encouraged to use larger doses of Choline Citrate compared to younger neurohackers.
Other versions of choline such as Alpha GPC and CDP-Choline will more readily cross the blood-brain barrier and make its way into your cells. So lower doses are required.
Choline Citrate Side Effects
Recommended dosages even for extended periods are considered well-tolerated and safe. While Choline Citrate is considered non-toxic, it is possible to experience toxicity with too much choline in your body.
If you experience trouble sleeping, headache, diarrhea, low or high blood pressure, nausea, blurred vision or chest pain – you should stop using Choline Citrate. Or reduce your dose.
Type of Choline Citrate to buy
Choline Citrate is sold in capsule or powder form. Capsules are usually 500 – 650 mg each. Some ready-made nootropic stacks, and even some brand name vitamins contain Choline Citrate in their formula.
Nootropics Expert Recommendation
Choline Citrate 500 – 3,000 mg per day
 I recommend using Choline Citrate as a nootropic supplement.
I recommend using Choline Citrate as a nootropic supplement.
Your body does not make Choline Citrate on its own. But some versions of choline naturally occur in your body and brain. Choline sources like Alpha GPC and CDP-Choline.
You do get some choline from the food you eat. But studies show we don’t get an adequate supply of choline from food sources in our modern diet. And as we age, our bodies have a difficult time using the choline we get from food.
Choline Citrate is especially helpful for those suffering from age-related cognitive decline. Studies show supplemental choline helps stop or reverse brain degeneration like Alzheimer’s Disease, and other cognitive disorders. Especially in the early to mid-stages of the disease.
I suggest starting with a dose of 500 to 1,000 mg daily. Choline Citrate is a good compliment to a stack including any nootropics from the racetam-family.
Piracetam for example affects your neuroreceptors for acetylcholine. So stacking Piracetam and Choline Citrate boosts acetylcholine activity even more.
If you’re on a tight budget and you need choline, Choline Citrate is a good place to start. It is one of the most affordable versions of Choline available. Particularly when purchased in bulk powder form. You just need more of it than other choline sources like Alpha GPC or CDP-Choline.
Use Choline Citrate at a ratio of 1:6. For example, 1,000 mg of Choline Citrate with 6,000 mg of Piracetam. If you get a racetam-headache add more choline to your stack.








Join The Discussion - 27 comments
Mek
September 1, 2024
Hello,
I have done a stool test to check for bacteria and the result was disbiosis. One of the problems are bacteria that produce trimethylamine (TMA) that is a precursor to TMAO. TMAO is a harmful molecule for cardiovascular health and inflammatory.
TMA is produced by bacteria that like choline, betaine and L-carnitine.
I got a recommendation to lower intake of choline, betaine, and L-carnitine (lower intake of meat, eggs and other stuff containing these nutrients).
Since I should not consume choline because of the bateria in my gut, is there an alternative like sublingual lozenges?
David Tomen
September 3, 2024
Mek, you need choline to produce acetylcholine. Disbiosis indicates a dysfunctional microbiome where bad bacteria are out of balance with good bacteria. This can be caused by medications like antibiotics, a diet high in processed foods, as well as psychological and physical stress. You should be working with your doctor to figure out what is causing this imbalance. Not trying to figure out how to reduce TMAO.
Maya
August 27, 2023
Hi David,
Sorry if I missed the answer to my question from someone else. I’m very intrigued with your experience with choline citrate for chronic shoulder pain. Would another form of choline help me as I cannot get hold of choline citrate here? If so, would a temporary higher dose do the trick of a different form of choline? Thank you for your help. Maya
David Tomen
August 31, 2023
Maya, I found that Choline Citrate was the only form of choline that helped. I found this one that is available in Canada: https://geni.us/Svsa
Maya
October 24, 2024
Hi David, thank you so much for sharing this information. When you found the choline citrate helpful for your muscle pain, can the higher dose be taken all at once or should it be taken throughout the day? Did you find it helped fairly quickly? ✨
David Tomen
October 25, 2024
Maya, when I was using Choline Citrate it was 500 mg 3-times per day as I recall. And it did help with muscle pain fairly quickly.