Table of Contents
Glycine (2-Aminoacetic Acid, Gly, G) is a conditionally essential amino acid and neurotransmitter. The simplest of all amino acids, glycine plays a role in the synthesis of nucleic acids, glutathione, RNA and DNA, and creatine.[i]
Glycine is synthesized in your body from threonine (through threonine dehydrogenase pathway), choline (via formation of sarcosine), and serine (through serine hydroxy methyltransferase [SHMT]).[ii]
Glycine is considered a “conditionally essential” amino acid because your body cannot produce enough on its own. So, the remainder must be obtained from foods like meat, fish, dairy, legumes, or supplements.[iii]
Glycine plays a critical role as a neurotransmitter because it controls your intake of food, behavior, and complete body homeostasis.
It can be both excitatory and inhibitory. Which means that it can stimulate your brain and nervous system, as well as quieten it.
Supplementing with glycine has been shown to effective in treating metabolic disorders, inflammatory disease, obesity, cancers, and diabetes.
Here we’ll investigate as a nootropic for enhancing sleep quality and brain function.
Glycine helps:
- Sleep: Glycine helps you fall asleep more quickly, reduce insomnia, improve sleep quality, and promote deeper and more restful sleep
- Neurological disorders: Glycine has been shown to be effective in those dealing with schizophrenia, OCD, and depression.
- Stroke: Patients who have suffered ischemic stroke (brain ischemia or cerebral ischemia), are given glycine orally to help limit damage to the brain within the first six hours of the stroke.
Overview
Glycine (2-Aminoacetic Acid, Gly, G) is one of the most important amino acids in your body. It helps in regulation of cardiovascular, cognitive, and metabolic health.
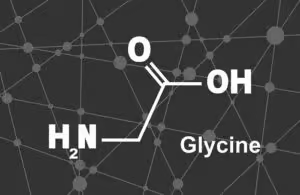 The name Glycine comes from the Greek word γλυκύς “sweet tasting“.
The name Glycine comes from the Greek word γλυκύς “sweet tasting“.
Glycine was discovered in 1829 by French chemist Henri Braconnot after boiling gelatin with sulphuric acid. And since then, it has been manufactured and distributed commercially as a sweetener, and as a buffering agent for antacids.
Glycine is also a sweet and colorless crystal that is synthesized in your body from choline, threonine, and serine.
As a therapeutic and nootropic supplement provides multiple benefits to human health.
Glycine has been shown to be effective for improving skin elasticity. And collagen peptide which is loaded with Glycine helps suppress sun-induced skin damage and reduce wrinkles around the eyes.[iv]
Glycine supplementation helps reduce the symptoms of schizophrenia.[v] It helps reduce symptoms of OCD. And low blood levels of glycine have been associated with depression.
Numerous studies have also shown glycine’s potential in improving sleep, enhancing memory, and increasing insulin sensitivity.
Glycine modulates inhibitory neurotransmitters via glycine receptors throughout the central nervous system.[vi] And potentiates NMDA receptors which provides an excitatory response.[vii] Affecting cognition, mood, immune function, and sleep.
How does Glycine work in the brain?
Glycine boosts brain health and function in several ways. But two in particular stand out.
- For sleep – Numerous studies have shown that glycine influences the quality of sleep, reduces insomnia, and promotes restful sleep. It does this in a couple of ways.
Glycine has a particular affinity for NMDA receptors and glycine receptors. Which results in increased peripheral blood flow, and a subsequent drop in the core body temperature.
In other words, glycine works to improve blood flow to the body’s extremities, which in turn reduces core body temperature.
This decrease in body temperature plays an important part of sleep induction since the onset of sleep is associated with lowered body temperature. Which then progresses to deep sleep.
Researchers demonstrated this in an animal study showing how glycine triggered a drop in body temperature which helped the study subjects fall asleep more quickly And spend more time in REM sleep. [viii]
The study also showed that glycine can help you experience deep, slow wave sleep more quickly.
Glycine has also been shown to increase the production of serotonin in the brain. Which helps sleep because serotonin aids in the synthesis of the sleep hormone melatonin.[ix]
Studies also suggest that glycine can help you get back to your regular sleep cycles after a period of a disrupted sleep schedule.[x]
- Schizophrenia – Glycine has shown promising results in reducing the symptoms of depression, OCD, anxiety, and bipolar disorder. However, its most pronounced efficacy is seen in the reduction of schizophrenia symptoms.
Post mortem evaluations of the brains of people with schizophrenia have shown fewer NMDA receptors compared to those who did not have the disease.
Researchers also found decreased levels of glycine in both the blood and cerebrospinal fluid of people with schizophrenia.[xi]
Glycine is known to be an NMDA agonist. It is well tolerated by the patients in both short-, and long-term treatment.
To date, numerous studies have been conducted to evaluate the efficacy of glycine in treating schizophrenia.
The first controlled trial used a glycine dose of 15 grams per day which showed significant improvement during glycine treatment.
Another study, 21 schizophrenic patients were given high doses of glycine in addition to antipsychotic treatment.
A significant 34% reduction in negative symptoms was observed during glycine treatment. And the study authors noted the improvement persisted even after patients stopped supplementing with glycine. [xii]
 How things go bad
How things go bad
Sleep deprivation or the inability to get a good night’s sleep is an increasing concern world-wide. Not enough sleep or poor sleep quality can result in:
↓ Memory loss
↓ Inability to concentrate
↓ Poor metabolism
↑ Weight gain
↑ Irritability
↑ High blood pressure
↑ High blood sugar levels
↓ Low sex drive
↑ Risk of heart disease
Glycine as a nootropic supplement helps the body make serotonin which improves sleep and mood. And it influences key receptors in the brain resulting in better learning and memory.[xiii] [xiv]
Low glycine levels in the body are also linked to depression.[xv]
 Glycine benefits
Glycine benefits
Glycine activates NMDA receptors in the brain and restores serotonin levels which helps improve sleep. And the ability to fall asleep faster.
In one study, 15 adult females were given either a placebo or 3 grams of glycine before bed.
The study concluded that supplementing with glycine showed a significant improvement in reduced fatigue, liveliness, and clear-headedness the next morning.[xvi]
Glycine helps brain cell signaling which boosts cognition, memory and mood.
Glycine taken in high doses has proven to be highly effective in reducing the symptoms of schizophrenia.
It helps with depression and mental fluency associated with schizophrenia.
And may improve psychotic symptoms as well.[xvii]
Evidence also suggests that glycine assists with depression and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Huntington’s.
Glycine also showed a protective effect against neurological damage associated with stroke.[xviii]
And research suggests improvements in memory, recall, and sustained attention in those supplementing with glycine as a nootropic.
How does Glycine feel?
People who take high quality glycine supplements report better sleep quality, and improved mood during the day.
Some users say they felt more balanced and livelier once they started supplementing with glycine.
Glycine is best taken 60 minutes before bed. Most users report a minimum of 7 hours of undisturbed, high quality sleep.
Glycine helps even chronic insomniacs fall asleep easily.
Unlike most sleep inducers, glycine does not leave you feeling groggy and fatigued in the morning. On the contrary, users wake up feeling rested and ready to tackle the day.
Glycine is a good joint health supplement. Because it aids in cartilage regeneration by enhancing collagen re-synthesis.
Glycine may also provide relief from night sweats for pre-menopausal and menopausal women.
 Glycine Clinical Research
Glycine Clinical Research
Glycine for schizophrenia
22 schizophrenic patients who were treatment-resistant took part in a double blind, placebo-controlled trial. They were administered 0.8g/kg per day of glycine along with their antipsychotic medication.
Clinical assessments were performed bi-weekly. The group who was administered glycine showed a 24-46% reduction in negative symptoms. [xix]
In another double-blind, placebo-controlled study, 14 medicated patients with chronic schizophrenia were treated with glycine. The results showed a significant improvement in negative symptoms in the group that was given glycine but not in the group given placebo. [xx]
Glycine for sleep
In a randomized placebo-controlled trial, 11 healthy adults were given either 3 grams of glycine or a placebo 1 hour before bed for 2 days. The results indicated quicker sleep onset followed by long, restful sleep.[xxi]
In 2012, another placebo-controlled study recruited healthy adults who were restricted to 25% less sleep than normal. Study subjects were given either a placebo or 3 grams of glycine before bed.
In subjects given glycine, the data showed a significant reduction in fatigue often related to reduced sleep.[xxii]
Glycine for learning and memory
Scientists studied the effects of bioglycin, a biologically active form of glycine in healthy students (mean age 20.7 years), and middle-aged men (mean age, 58.9 years).
The researchers specifically measured attention, memory, and mood using a double-blind, randomized design. [xxiii]
The results indicated that bioglycin significantly improved episodic memory in both the young and middle-aged group. And the middle-aged group also showed a significant improvement in the sustained-attention task.
Glycine Recommended Dosage
 Recommended nootropic dosage of Glycine is 3 grams per day.
Recommended nootropic dosage of Glycine is 3 grams per day.
Experts recommend a Glycine dosage of 0.4 grams per kilogram of body weight (g/kg) twice daily when taking an atypical antipsychotic like Zyprexa and Risperdal.
Many human trials have safely used glycine doses of 1 g (1000 mg) per day for supporting brain health after a stroke. And up to 50 grams per day for schizophrenia.
Most Glycine supplements come in 1000 mg capsules. And the most effective dose is reported to be 3 grams 60 minutes before bed.
Glycine Side Effects
Glycine supplements are generally considered non-toxic and safe with few side effects in most people.
However, supplementing with 9 grams or more of Glycine may result in mild gastrointestinal symptoms such as an upset stomach, nausea, loose stools, or vomiting.
Slight sedation is also a possible side effect of taking glycine.
Do not take glycine if you are on the antipsychotic drug Clozaril (clozapine). Unlike other drugs used to treat schizophrenia, glycine appears to decrease the effectiveness of Clozaril in some people.[xxiv]
Do not use glycine if you are suffering from diarrhea, as it may worsen the condition.
Due to lack of sufficient research, glycine should be avoided by breastfeeding and pregnant women unless prescribed by a physician.
Type of Glycine to Buy
Glycine is available in 1000 mg capsules, 500 mg tablets, and as powder.
Look for a Glycine supplement with zero “other ingredients”.
Avoid Glycine supplements containing additives such as silicon dioxide, stearic acid, or magnesium stearate.
I recommend: Click for Life Extension – Glycine because it is pure.
Nootropics Expert® Recommendation
I recommend Glycine as a nootropic supplement.
Your body makes some Glycine during the day. But you need more Glycine than your body can produce on its own. So, you must get it from food or a nootropic supplement.
Glycine is particularly effective in those dealing with sleep disorders or insomnia.
Supplementing with Glycine should provide a good night’s sleep. And have you feeling well-rested the next morning.
Glycine has been shown to be effective in those dealing with schizophrenia. Even while using most regular medications used with this disorder.
But please, if you are dealing with schizophrenia, check with your doctor before using this nootropic.
Glycine as a nootropic supplement used at recommended dosages is non-toxic and safe for most people with little or no side effects.
3 grams of Glycine seems to be most effective for most people taken about 60 minutes before bed.
I recommend: Click for Life Extension – Glycine because it is pure.







Join The Discussion - 152 comments
Tania Curiel
October 29, 2024
Hi,
I took Glycine 1.5 g before bedtime and had a better and restful sleep that night. The next day I took 3 g because I read it is the right dosage for sleep, and I had again better sleep but little less than the night before. But the next 3 nights with the 3 g dosage my sleep has been bad as if the glycine had stopped working or even had the opposite effect. Should I lower the dose or on the contrary increase it? Thank you
David Tomen
October 30, 2024
Tania, if that was your reaction then definitely reduce the dosage. If 1.5 grams before bed worked for you then continue with that dosage and timing. If it starts to interfere with sleep then cut the dose in half. If that does not help then find another supplement.
Tania
October 31, 2024
Thank you!!
André
July 30, 2024
Dear David,
is it OK to take N-dimethyl glycine instead of ordinary glycine?
Best regards
André
David Tomen
July 30, 2024
André, why do you want to use that instead of Glycine? I have not done the research on that specific derivative of glycine so cannot make an intelligent suggestion.
Mick
July 27, 2024
Hi David,
Would you recommend using Glycine for me? And if you do, which dosage is the best for me?
I’m diagnosed with paranoid schizophrenia. It is under control. I’m taking Clozapine 200mgs before bed.
What do you think the best thing to do in my situation?
Thanks.
David Tomen
July 30, 2024
Mick, the recommended nootropic dosage of Glycine is 3 grams per day. Clinical studies with schizophrenia used 15 grams of Glycine per day but you do not need to use that high of a dose if you are using it daily and long-term.
Mick
July 31, 2024
Ok David, thanks a lot for the advice.
On your site you mentioned that if a person takes clozapine its better not to take Glycine. 3 grams is not a big dosage, do you think it’s ok for me to take it?
David Tomen
August 1, 2024
Mick, glycine appears to decrease the effectiveness of clozapine in some people. So, if you feel your symptoms come back then you should stop using glycine.
Mick
August 1, 2024
Okay, thank you for the tip, David!
Warren
July 3, 2024
Hey David, how long does the glycine last in the body after ingestion?
David Tomen
July 6, 2024
Warren the half life of Glycine is dose dependent: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8212419/.
Brad
April 15, 2024
TMG Could it be an effective and bioavailable source of glycine? Is it also a nootropic?
David Tomen
April 22, 2024
Trimethylglycine (also called betaine) is a methyl derivative of glycine. I have not researched TMG. But if someone wanted the benefits of using Glycine then why not just use Glycine?
Roman
April 6, 2024
If Glycine potentiates NMDA which is excitatory, then how it improves sleep quality when sleep and excitation are opposite concepts.
David Tomen
April 8, 2024
Roman, Glycine is both excitatory and inhibitory. Which means that it can stimulate your brain and nervous system, as well as quieten it.
salem
March 24, 2024
Hi David
i read that as Cholic Acid & Chenodeoxycholic Acid make up 80% of all bile acids
72-76% of BOTH are conjugated with GLYCINE , and just 25% with Taurine
so should Glycine and Taurine be taken with a ratio of 3:1 ?
like 3g of Glycine with 1g of taurine
is that right ?
David Tomen
March 29, 2024
Salem, forget about ratios because this could vary from person to person. Better to follow dosage recommendations for each supplement.
Lewis
October 7, 2023
Great article thank you!
why do I feel if I take 3-4g in the evening I have zero libido the next day? Like I feel calm and great but no interest in sex at all.
Also: how much glycine is in Mg Glycinate supplements?
Thank you
David Tomen
October 10, 2023
Lewis, it is affecting your sex hormones. Often when using a high dose of a supplement like an amino acid (which in this case is a conditionally essential amino acid which means your body produces some on its own but the rest needs to come from food of a supplement) it upsets the ‘natura’ balance of something. It could be the amino acid precursors needed to make glycine internally get out of whack because they are not being use to make Glycine. Etc.
There is not a definite way to point to the cause. This is only an example of what could be happening. It sounds like if you do not like the loss of interest in sex then either take a smaller dose or quit this supplement altogether.