Table of Contents
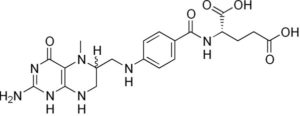
Vitamin B9 (Folate, folic acid, 5-methylenetetrahydrofolate) is water-soluble, and one of 8 B-Vitamins.
Folate functions as a coenzyme in single-carbon transfers in the synthesis of DNA and RNA. And converts homocysteine to methionine which is used in the synthesis of S-Adenosyl-methionine (SAMe).[i]
As a nootropic, folate is also involved in gene expression, amino acid synthesis, myelin synthesis, and is required for the synthesis of the neurotransmitters dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine and serotonin.
Many neurohackers, including doctors and other health professionals confuse folate with folic acid. They are NOT the same.
In this article, we’ll explore the differences between folate and folic acid. And how Vitamin B9 (folate) is critical for the fully optimized brain.
Vitamin B9 (Folate) helps:
- Brain Optimization: Folate is involved in DNA and RNA synthesis, gene expression, amino acid synthesis and metabolism, and myelin synthesis and repair.
- Neurotransmitters: Folate is required for the synthesis of dopamine, epinephrine and serotonin.
- Mood: It is thought within research circles that folate’s involvement in neurotransmitter synthesis is most responsible for mood and cognition. Even increasing the effect of SSRI’s in those being treated for depression.
What is Vitamin B9 (Folate)?
Vitamin B9 (Folate, folic acid, 5-methylenetetrahydrofolate) is water-soluble, and one of 8 B-Vitamins.
Folate is a critical component of DNA and RNA synthesis, gene expression, amino acid synthesis, and myelin synthesis and repair. Folate is required as part of the cycle that produces most of your major neurotransmitters including dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine and serotonin.
Folate is used in red blood cell production, helps the break down and use of proteins, and just about every other process in your body.
Folate deficiency is found in at least a third of those suffering from depression. Folate touches nearly everything happening in your brain. And the reason why we’re investigating it here. Folate should be part of your nootropic stack.
Green leafy vegetables, or ‘foliage’ are rich sources of folate. And how ‘folate’ got its name. You can also get folate from citrus fruit juice, legumes, fortified foods and liver.
When you eat vegetables containing folate, or eat flour-enriched with folic acid, an enzyme called MTHFR (5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase) converts folic acid and food folate into 5-methylenetetrahydrofolate (methyl-folate or 5-MTHF).
Folate is a general term for a group of various tetrahydrofolate (THF) derivatives naturally found in food. Folic acid refers to an oxidized synthetic compound used in many dietary supplements and for food fortification.
Natural Tetrahydrofolate (THF)can enter the natural folate metabolic cycle which begins in the mucosa of your small intestine. But synthetic Folic acid on the other hand, begins its initial reduction and methylation in your liver, where conversion to the THF form requires the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase.
One of the problems with choosing the unnatural and synthetic form of folic acid is when you have low activity of the dihydrofolate reductase enzyme, and then combine that with a high intake of folic acid, you end up with unnatural levels of unmetabolized folic acid entering your bloodstream.
Several studies have reported the presence of this unmetabolized folic acid in blood following consumption of folic acid supplements, or folic acid-fortified food.[ii]
We have growing evidence in Western society that we generally test for excess levels of unnatural folic acid. Because we are eating processed foods fortified with folic acid, and folic acid-enriched flour. And we still suffer from a folate deficiency.
High doses of synthetic folic acid may increase your risk of cancer, immune system damage and other really nasty health problems.[iii]
Problems with MTHFR
Another major problem causing folate deficiency is problems with the MTHFR gene. Recall that this enzyme called MTHFR (5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase) is needed to convert folic acid and food folate into 5-methylenetetrahydrofolate.
There are two common variants in this gene which causes problems with the functioning of MTHFR. They are called C677T and A1298C. Both variants are genetically inherited. And if you inherited either of these mutations, ti will decrease the effectiveness of MTHFR from 30 – 70%. Which is another cause for folate deficiency.
Estimates of the prevalence of these mutations in our general population are up to 60%. Some doctors report that nearly every patient in their practice have one or both MTHFR mutations.[iv]
And we have clinical evidence of the association between both MTHFR mutations in depression, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia.[v]
Folate is one very busy molecule in your body:
- Folate donates a methyl group to homocysteine to produce SAMe. The methyl donor SAMe is involved in the formation of phospholipids, glutathione, myelin, coenzyme Q10, carnitine and creatine in your brain
- Folate synthesizes the enzyme cofactor biopterin (BH4) which is critical for the synthesis of major neurotransmitters including dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine and serotonin
- Folate is requir3ed for the synthesis of DNA and tRNA
- Folate recycles and reduces the inflammatory amino acid homocysteine
- Folate is a cofactor in the production of red and white blood cells and platelets.
How does Vitamin B9 (Folate) work in your brain?
Vitamin B9 (Folate) boosts brain health and function in several ways. But two in particular stand out.
- Folate influences neuroplasticity and neurotransmitters. Folate is required for the synthesis of the neurotransmitters dopamine, epinephrine, and serotonin.
The active metabolite of folate called 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF, L-methylfolate), participates in re-methylation of the amino acid homocysteine, creating methionine. S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe), the downstream metabolite of methionine is involved in numerous biochemical methyl donation reactions, including reactions forming the above-mentioned neurotransmitters.
Without the participation of 5-MTHF in this process, SAMe and neurotransmitter levels decrease in your cerebrospinal fluid, which then contributes to the disease process called depression.
Studies have shown that if you are being treated for depression with SSRI antidepressants, and you are not responding to these drugs, you may get a much better response by taking folate to your antidepressant med.[vi]
- Folate helps reduce depression. Folate is involved in one-carbon metabolism in your brain. This folate cycle is responsible for the synthesis of methyl groups which are used by SAMe in several methylation reactions involving nucleoproteins, proteins, phospholipids, neurotransmitters and monoamines.
Deficiency in both folate and Vitamin B12 will impair methylation processes. Causing the accumulation of homocysteine. Low concentrations of folate in your blood, red blood cells and cerebrospinal fluid are associated with depression and dementia.
Research shows that cognitive function is related to methylation processes in your brain.[vii] This depression hypothesis is supported by the similar effect of SAMe on monoamine neurotransmitter metabolism, which is also implicated in depression.[viii]
The lowest concentrations of folate and SAMe in cerebrospinal fluid are found in dementia, including Alzheimer’s Disease.[ix]
How things go bad when you are folate deficient
Methyl-folate (5-MTHF) works with Vitamins B2, B6 and B12 as well as cofactors like magnesium in this methylation cycle in every cell in your body and brain.
The metabolic process called methylation occurs when one molecule provides a methyl group, which is a carbon atom linked to three hydrogen atoms, to another molecule. And is required to produce creatine, carnitine, CoQ10, phosphatidylcholine (PC), melatonin and a bunch of other critical neurotransmitters and functions in your body.
Methylation is involved in cognition, repairing DNA, turning genes on and off, fighting infections and inflammation, getting rid of toxins and much, much more.
Problems with methylation (which can be caused by not enough folate) can contribute to addictions, Alzheimer’s, anxiety, ADD and ADHD, bipolar and manic depression, chronic fatigue syndrome, dementia, diabetes, fibromyalgia, schizophrenia, and hypothyroidism.
Methylation is not only involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters, but breaking them down as well. This critical step, when broken, causes a buildup of neurotransmitters that can lead to seizures, insomnia, panic attacks, fits of rage, and more. Much more.
A deficiency in methyl-folate (5-MTHF) in your body caused by problems with this methylation pathway leads to a deficiency of glutathione, the master antioxidant supporting your immune system. This deficiency can take shape as fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue, increased immune activation, chemical sensitivities and even diseases like ALS, MS, and Parkinson’s.
Not enough folate and you can experience:
↓ Mitochondrial dysfunction[x]
↓ Depression, mood and social function decline
↓ Cognitive function declines
↓ Concentration, cognition and memory declines
↑ Risk of Alzheimer’s and dementia increases
↑ Risk of anemia increases
↑ Irritability, forgetfulness, and mental sluggishness increases
Vitamin B9 supplementation can help increase the density of serotonin and dopamine in your brain. And improve neurotransmitter signaling. Helping you to cope with stress, reduce depression and improve your memory.
Vitamin B9 (Folate) benefits
Depression affects about a quarter of the US population who expereince at least one depressive episode in their lifetime. (My apologies to our readers from other countries. I only have statistics for the USA).
 But world-wide, folate deficiency is found in at least a third of those suffering from depression. And research shows that folate levels even in the “normal range” might be inadequate for methyl donation and neurotransmitter synthesis.
But world-wide, folate deficiency is found in at least a third of those suffering from depression. And research shows that folate levels even in the “normal range” might be inadequate for methyl donation and neurotransmitter synthesis.
By adding methyl-folate to your nootropic stack, you’re adding a necessary ingredient for the synthesis of the neurotransmitters dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine and serotonin.
The active metabolite of folate called 5-MTHF or L-methyl-folate participates in the re-methylation of the amino acid homocysteine creating methionine. SAMe which is the downstream metabolite of methionine is involved in several methyl donor reactions, including the production of most major neurotransmitters.
Methyl-folate also seems to save the day by stepping in, and substituting for tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), which is an essential cofactor in neurotransmitter synthesis (when your BH4 is low).
The bottom-line: folate helps boost alertness, attention, cognition, memory, and mood. And helps alleviate brain fog, anxiety and depression.
How does Vitamin B9 (Folate) feel?
Up to 60% of us do not produce enough of the enzyme needed to break down synthetic folic acid found in supplements and fortified foods like breakfast cereal and bread. And the simple presence of this impostor in your diet is likely contributing to many of our modern diseases.
Neurohackers report that supplementing methyl-folate:
- Boosts alertness and energy levels
- Relief from chronic pain
- Tolerance for heat increases
- Sociability increases
- Relief from depression, fatigue and paranoia
- Fewer headaches
- Mental clarity increases
- Much happier, calmer, more energetic
- Gingivitis and gum inflammation decreases
Vitamin B9 (Folate) Clinical Research
Folate as an Antidepressant
Many who use antidepressants experience little to no relief in depression symptoms. And researchers set out to find out why antidepressant meds were not working.
Dr. Jerome Sarris of the University of Melbourne did a meta-analysis of clinical trials using ‘nutrients’ as a keyword along with antidepressants in PubMed, CINAHL, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science up to 2015.
The research team found that Omega-3’s combined with antidepressants boosted the success of using meds for depression. The team also found strong evidence for methyl folate, Vitamin D, and SAMe.
Dr. Sarris’ research showed that using folic acid or inositol provided zero benefit. The team concluded there was strong evidence supporting the use of methyl folate, Omega-3, Vitamin D and SAMe with antidepressants to reduce depression.[xi]
Another study in Milan compared using methyl-folate with the antidepressant Trazadone. 96 patients with dementia received either 50 mg of methyl-folate per day, or 100 mg of Trazadone.
After 4 weeks of treatment, depression scores for the methyl-folate patients decreased more than for the Trazadone patients.[xii]
Folate Reduces Risk for Dementia
Folate deficiency is associated with tripling the risk of developing dementia among elderly people. Researchers tracked 518 people over the age of 65 for 2 years for dementia development. The study found that the onset of dementia was much more likely in those whose folate levels fell over 2 years.[xiii]
Another study published in the British Medical Journal looked at the neurological status of 24 folate-deficient patients compared with a control group of 21 normal folate-level patients.
The study showed a significant increase in organic brain syndrome in the folate-deficient group.[xiv] Organic brain syndrome is a general term used to describe decreased mental function caused by something other than psychiatric illness.
Vitamin B9 Improves Memory
A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association evaluated nutritional status and cognitive function in 260 men and women older than 60 years. The study showed there was a significant relation between impaired abstract thinking ability and memory, and lower folate levels and intake.[xv]
In another open study of 38 folate deficient subjects with depression, lethargy, and memory impairment, 50 mg of folinic acid per week for 120 days significantly improved visuomotor performance, visuospatial memory, logical reasoning, associative memory, and activities for daily living.[xvi]
Vitamin B9 (Folate) Recommended Dosage
Recommended dosage for Vitamin B9 (Folate) is 500 mcg.
If you decide to add folate to your nootropic stack, start with Vitamin B12 as methylcobalamin. And then introduce your dose of methyl-folate along with the cofactors Vitamin B2, Vitamin B3, Vitamin B6, trimethyl glycine, and Vitamin C
If you have an adverse reaction to methyl-folate (agitation, increased anxiety, headache), you can take Vitamin B3 (nicotinic acid or niacinamide) in 50 mg dosages every 30 minutes until you experience relief.
Note that Vitamin B3 (niacin) requires SAMe for its metabolism. And can contribute to a drop in methylation if you’re low in SAMe. It is also a cofactor for the enzyme COMT that breaks down norepinephrine, epinephrine, and estrogen, which are all potentially elevated if you are experiencing anxiety.
Vitamin B9 (Folate) Side Effects
Vitamin B9 (Folate) is non-toxic. So is considered well-tolerated and safe.
But note that higher doses of Vitamin B9 like those used in clinical trials nearly always use synthetic folic acid. If you are deficient in Vitamin B12, and many people are, it can manifest as anemia. And looks just like folate deficiency.
Large doses of folate could correct anemia. But without correcting an underlying Vitamin B12 deficiency, it can leave you at risk for irreversible brain damage.
This is why the US Institute of Medicine advises that all adults limit their intake of folic acid supplements to 1 mg daily.
Note that it is unlikely that you’ll encounter this problem by using folate or methyl-folate instead of folic acid. But I don’t have the science yet to back this claim up.
High concentrations of unmetabolized folic acid in your blood, especially if you’re low in Vitamin B12, could result in a compromised immune system. And problems with cognition.
Other side effects from supplementing folic acid, particularly in high doses can include stomach problems, insomnia, skin reactions, confusion, loss of appetite, nausea and seizures.
Many medications interfere with folic acid absorption including antibiotics, Dilantin, Daraprim, chemo meds, antacids, proton pump inhibitors, anti-seizure medications, NSAIDS (ibuprofen and naproxen), Azulfidine, and Methotrexate.
Vitamin B9 (Folate) types to buy
Vitamin B9 (Folate) is available in capsules, softgels, and in powder form.
Studies have shown that the active form of folate, methyl-folate, which is more easily absorbed, and easily crosses the blood-brain barrier, may be effective in the prevention and treatment of depression and dementia.[xvii]
Look for a folate supplement that says “L-methylfolate”, “5-methyltetrahydrofolate” or “5-MTHF” on the label. The patented forms called Quatrefolic® or Metafolin® are one method for ensuring the supplement’s purity and effectiveness.
One great option to ensure you are getting all the vitamins and cofactors you need for the methylation cycle is to use a BioActive B-Complex.
The Performance Lab® B-Complex offers a nature-identical form of Vitamin B9 (folate) and is now my favorite daily B-Complex supplement.
I prefer the Performance Lab® B-Complex because it’s more potent, it’s biologically active and I’ve found to be a far more effective compared to every other B-complex supplement I’ve used.
Performance Lab® uses their own priority NutriGenesis® vitamins and minerals which are grown on probiotic, plant and yeast cultures in a state-of-the-art lab.
Avoid any product, including multivitamins of B-Vitamins or B-Complex Vitamins, which list “folic acid” on the label.
Get: Performance Lab® B-Complex
Nootropics Expert Recommendation
Vitamin B9 (Folate) up to 500 mcg per day
 I recommend using Vitamin B9 (Folate) as a nootropic supplement.
I recommend using Vitamin B9 (Folate) as a nootropic supplement.
Your body does not make Vitamin B9 on its own. So you must get folate from food or a supplement.
Vitamin B9 (Folate) is especially helpful for those suffering from anxiety, depression, panic attacks, or OCD. Folate can help reduce insomnia, and help increase energy levels.
Experience shows Vitamin B9 helps stop and reverse the symptoms associated with high homocysteine levels.
Vitamin B9 is also particularly helpful to quell anxiety caused by social situations.
Vitamin B9 can help you get a good night’s sleep. You may find it as effective as sleep meds and other nootropics used for sleep. You’ll awaken feeling refreshed and calm. Ready to start your day.
The recommended dosage of Vitamin B9 (Folate) is up to 1,000 mcg per day. Start low at 500 mcg and see how your body reacts.
Please refer to Recommended Dosage section of this article for adding the other B-Vitamins to your stack for an optimal methylation cycle. Your neurotransmitters are counting on it.
At the very minimum every neurohacker should be using a multivitamin every day that includes Vitamin B9 (folate but NOT folic acid!). The best multi I’ve found and use every day is the Performance Lab® NutriGenesis Multi for men or women.
And I recommend the Performance Lab® B-Complex if your looking for a B-Vitamin Complex








Join The Discussion - 109 comments
Gary Smith
May 25, 2025
Hi David,
I read this on a website about the most bioavailable methylfolate forms. Do you have any feedback or thoughts?
The higher the bioavailability, the more of it your body can actually use.
➡️ Magnafolate®: About 78% bioavailable.
➡️ Metafolin®: Between 74-77% bioavailability.
➡️ Extrafolate-S®: Between 72-74% bioavailability.
➡️ Quatrofolic®: About 50% bioavailable.
➡️ Cerebrofolate®: About 81-82% bioavailability. (coming soon) ✨
David Tomen
May 26, 2025
Gary, if the person who posted that has done their research it is easy enough to verify if there are accurate. You can go to each manufacturers website and see if they make any claims about bioavailability of their product. If you cannot find this kind of info then the person who posted this made it up.
Unknown
May 16, 2025
I’d like to clarify. How long does it take for B vitamins to be excreted. For example, if I take B6 at night, will it still be there in the morning to produce Sam-E, or do I need to take it again?
Thanks so much in advance, I’m sure you’ve been told a thousand times, but you’ve done a great job, I haven’t found anything even close to similar quality.
Is there a new nootropic coming soon? I can’t wait)
David Tomen
May 16, 2025
Water soluble vitamins leave your body but the length of time for excretion varies. Studies show that if you consume B-Vitamins daily you’ll maintain your levels. It does not matter what time of day. The key is “daily”.
I’ll be adding new nootropics to the list over the next 2 – 3 months. They will likely be known to most in this community. But they will be “new” to the nootropics list. Examples will be Selank, Semax, Vitamin B2, etc.
__Unknown__
May 17, 2025
Thanks