Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Acetyl-L-Carnitine (ALCAR) is a synthesized version of L-Carnitine that enhances energy production, supports fat burning, and improves cognitive function.
- ALCAR facilitates fatty acid transport to mitochondria, boosts acetylcholine formation, and exhibits antioxidant properties.
- ALCAR benefits brain health by supporting mitochondrial function, protecting brain cells, and improving cerebral blood circulation.
- It has potential therapeutic effects on conditions such as Alzheimer’s, dementia, Parkinson’s, depression, and mild cognitive impairment.
- ALCAR supplementation dosage recommendation is 500 – 1,500 mg per day depending on the desired goal. If you’re in a hurry, you can get an effective dose of ALCAR in this supplement: Click for Performance Lab® Energy
Acetyl-L-Carnitine (ALCAR, ALC or LAC) is a synthesized version of L-Carnitine. Which is a derivative of the amino acids lysine and methionine.
ALCAR is more bioavailable than L-Carnitine. It easily crosses the blood-brain barrier. And delivers L-Carnitine across cell membranes and into your brain (which L-Carnitine would not be able to cross on its own).
L-Carnitine is naturally made in your liver and kidneys. And then transported to other tissues including your brain and heart.
ALCAR helps:
- Brain Energy Metabolism. ALCAR helps facilitate fatty acid transport to the mitochondria where they’re needed for producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Fatty acid metabolism fuels your cells and can boost physical and mental energy. This also assists with fat burning in other cells.
- Neurotransmitters. ALCAR is a necessary ingredient for acetylcholine formation. Which boosts memory, mental alertness, and fluid thought.
- Brain Optimization. The antioxidant properties of Acetyl-L-Carnitine provides neuroprotective qualities, boosts Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF), and promotes cerebral blood circulation.
Acetyl-L-Carnitine (ALCAR) Overview
L-Carnitine is an amino acid that’s synthesized in your body. You also get it from red meat and dairy.
 L-Carnitine is considered a “conditionally essential” nutrient because when your body uses it faster than it can produce it, you need supplemental L-Carnitine either from food or a supplement.
L-Carnitine is considered a “conditionally essential” nutrient because when your body uses it faster than it can produce it, you need supplemental L-Carnitine either from food or a supplement.
L-Carnitine is used throughout your body. Here we’re talking about the Acetyl-L-Carnitine form of L-Carnitine because of its affects on brain health and chemistry.
L-Carnitine vs. Acetyl-L-Carnitine: What’s the Difference?
L-Carnitine and Acetyl-L-Carnitine are often referred to as Carnitine. But each are structurally different, and each has its advantages.
L-Carnitine: Helps produce energy within the mitochondria of your cells, but is not capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier. Supplemental L-Carnitine is difficult for your body to absorb; only 18% of it reaches your bloodstream.
L Carnitine supplements are favored by athletes and dieters who want Carnitine’s fat-metabolizing benefits. But are not seeking any brain benefits.
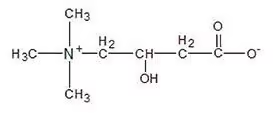
Acetyl-L-Carnitine: Is easier to absorb and used by your body than L-Carnitine. In one animal study, who were given 2 grams of ALCAR daily for 50 days, ALCAR boosted blood levels of ALCAR by 43%.[i]
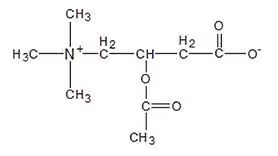
ALCAR does everything that L-Carnitine does, but by adding an acetyl group, it but can also cross the blood-brain barrier. In another animal study, researchers found that ALCAR supports mitochondrial function which then protects brain cells from oxidative stress, while L-Carnitine does not.[ii]
How does Acetyl-L-Carnitine Work in the Brain?
Acetyl-L-Carnitine boosts brain health and function in several ways. But two in particular stand out.
- ALCAR boosts acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter tied to memory and overall brain function. Acetyl-L-Carnitine is a precursor to acetylcholine in the presence of Coenzyme-A. Test tube studies shows that ALCAR donates a “acetyl group” to help make acetylcholine.[iii]
Alzheimer’s-diseased brains show a 25% to 40% reduction in carnitine acetyltransferase, an enzyme that works with L-Carnitine & Acetyl-L-Carnitine.
This enzyme decline led researchers to link low ALCAR with low acetylcholine, and Alzheimer’s onset. They went on to suggest that the therapeutic properties of ALCAR supplementation is a viable therapy for brain regeneration.[iv]
- ALCAR promotes brain energy metabolism by supporting your brain cell’s mitochondria in creating ATP which is your main source of cellular energy.[v]
ALCAR works as a shuttle transport for fatty acids through cell membranes into mitochondria to assist with adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthesis.[vi]
ALCAR is essential for fatty acid oxidation:
- ALCAR shuttles fatty acids into mitochondria, for the creation of ATP.
- ALCAR then shuttles fatty acids out of mitochondria, and flushes out tox ic byproducts.
ALCAR helps maintain mitochondrial function in nearly every cell of your body. Your brain consumes at least 20% of your body’s energy. And generates a lot of toxic byproducts as well as different chronic intermittent stressors. . So ALCAR supplementation is particularly important for a healthy brain.
How things go bad
As we get older, our brain chemistry and energy metabolism changes.[vii]
↓ Nerve growth factor in the brain declines
↓ Acetyl-L-Carnitine levels decline
↓ Acetylcholine levels decline
↓ Mitochondria loses efficiency
All of these age-related changes are contributing factors to cognitive impairment and the neurodegenerative diseases of aging, including Alzheimer’s and dementia.
ALCAR Nootropic benefits
Animal research conducted at the Linus Pauling Institute at Oregon State University shows that Acetyl-L-Carnitine will:[viii]
- Restore efficient mitochondrial energy production
- Replenish age-related changes to mitochondrial structure
- Replenish ALCAR and acetylcholine levels in the brain and body
One of the most potent Acetyl-L-Carnitine benefits is that it has the ability to boost acetylcholine and rejuvenate brain cells (including mitochondria). This has been proven to benefit those with age-related brain diseases like Alzheimer’s and major depressive symptoms.[ix]
And one animal study conducted in New Delhi showed that Acetyl L-Carnitine reduces lipofuscin in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, striatum and thalamus.
How does Acetyl-L-Carnitine feel?
You may not feel ALCAR… unless you’re elderly, have low energy levels, or have Erectile Dysfunction. Within those specific groups, users of Acetyl-L-Carnitine report it helps with memory, mental fatigue, mood, mental performance and the ability to get and maintain an erection.
 ALCAR’s brain support and its ability to support the mitochondria in your brain cells should boost cognition in all age and gender groups.
ALCAR’s brain support and its ability to support the mitochondria in your brain cells should boost cognition in all age and gender groups.
As a nootropic, ALCAR user reviews report a boost in energy and quicker thinking.
ALCAR Clinical Research
In one study, researchers showed that ALCAR may have beneficial effects for depression and dementia in the aging brain.[x]
Another study out of Italy; researchers showed that Acetyl-L-Carnitine stimulated the growth of new neurites. More of these minute projections from nerve cell bodies meant increased signaling between cells throughout the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord).[xi]
And a study conducted at the Mount Sinai School of Medicine in New York found that ALCAR has potential in treating the symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease. By directly affecting mitochondrial respiration and assisting dopamine receptors and the use of dopamine in the brain.
ALCAR helps with Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI)
A gold-standard double-blind, randomized controlled trial on 1,204 people showed significant effect on attention, mental performance, memory and higher mental functions.[xii]
In this study ALCAR seemed to ward off further brain deterioration. And could be considered as therapy for brain degeneration.
Acetyl-L-Carnitine slows rate of cognitive decline
130 Alzheimer’s patients were given ALCAR or a placebo daily for a year. They were tested across 14 points of cognitive performance.
This research showed a slower decline in cognitive performance with the ALCAR group compared to the placebo group.[xiii]
ALCAR effective for Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
 Acetyl-L-Carnitine has been shown to improve fatigue in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome.
Acetyl-L-Carnitine has been shown to improve fatigue in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome.
In a randomized, double-blind, crossover study; 36 people were treated for 3 months with either amantadine (used to treat Chronic Fatigue), or 1 gram of ALCAR twice daily.
The results of the study showed that ALCAR was better tolerated and more effective for brain function than the pharmaceutical for fatigue.[xiv]
Acetyl-L-Carnitine protects from oxidative damage of Ecstasy (MDMA)
Research has shown ALCAR to be effective in protecting your mitochondria from oxidative stress. But these guys took it a step further.
Male rats were given Acetyl-L-Carnitine before a dose of Ecstasy (MDMA). ALCAR pretreatment “exerts effective neuroprotection against MDMA-induced neurotoxicity at the mitochondrial level”, said the researchers.[xv]
Keep that in mind before your next party.
ALCAR for Erectile Dysfunction?
Carnitine versus androgen administration. In this study, 120 patients were split into 3 groups. Group 1 was given 160 mg
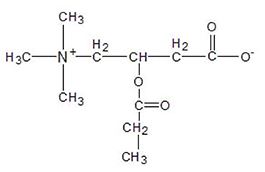
of testosterone per day. The 2nd group was given 2 grams of Propionyl-L-Carnitine plus 2 grams of Acetyl L Carnitine hcl per day. And the 3rd group a placebo.
Did you know that there’s an International Index of Erectile Function?
Turns out the Propionyl-L-Carnitine/Acetyl-L-Carnitine stack was better than testosterone for sexual dysfunction. Without the side effects of an enlarged prostate, better orgasms, more sexual desire and improved mood.[xvi]
ALCAR Recommended Dosage
- Acetyl-L-Carnitine suggested dosage for cognitive benefits is 1 – 4 grams per day.
- For improved mood and elimination of chronic fatigue, 1 – 3 grams of ALCAR per day.
- For age-related memory concerns, 1 – 2 grams of ALCAR per day.
ALCAR is water-soluble and can be taken on an empty stomach with water. A few supplement manufacturers recommend taking their Acetyl-L-Carnitine with a meal. Which may imply that it’s fat-soluble although I’ve found no evidence in the scientific literature.
ALCAR Side Effects
Acetyl-L-Carnitine is produced naturally in your body. So is considered well-tolerated and safe.
Side effects are rare but can include nausea, vomiting, increased agitation, weight loss, and restlessness.
You can also see an increase in seizure frequency if you have any kind of seizure disorder.
ALCAR and thyroid hormones. L-carnitine inhibits both triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) entry into the cell. Which means ALCAR supplementation may make thyroid hormone replacement therapy less effective. But could also help someone suffering from hyperthyroidism.
Types of ALCAR to buy
- Acetyl-L-Carnitine: L-Carnitine with an extra acetyl group. This version of l carnitine is more bioavailable and easily crosses the blood-brain barrier.
- L-Carnitine: This is the standard form of l carnitine found in food.
- Lipo-Carn®: A proprietary blend of Alpha-Lipoic Acid and Acetyl-L-Carnitine. Studies show this combination is a powerful anti-aging duo.

Performance Lab Energy contains an effective dose of ALCAR Together, these two help combat diabetes, glucose metabolism, boost energy production, lower high blood pressure, fat metabolism, maintain proper cognitive function, protects the body from radiation and chemical toxins and helps immunity.[xvii]
- Propionyl-L-Carnitine: L-Carnitine combined with propionic acid. This form is noted for its antioxidant activity, reducing oxidative stress biomarkers, and is used for heart health applications. Also useful for erectile dysfunction.
- Biosint™ is pharmaceutical grade Acetyl-L-Carnitine that is manufactured in Italy by Sigma Tau HealthSciences
You can also get 500 mg Acetyl L-Carnitine, 100 mg BioEnhanced™ R-Lipoic Acid, 100 mg CoQ10, 10 mg BioPQQ®, and 2.5 mg BioPerine® in one dose of my favorite energy supplement Click for Performance Lab® Energy .
Nootropics Expert Recommendation
Acetyl-L-Carnitine 500 – 1,500 mg per day
 I recommend using Acetyl-L-Carnitine as a nootropic supplement.
I recommend using Acetyl-L-Carnitine as a nootropic supplement.
Your body does synthesize some ALCAR on its own. And from the food you eat. But most L-Carnitine comes from red meat. And unless you eat a lot of great quality grass-fed beef or mutton you can not produce sufficient amounts, and likely have an Acetyl-L-Carnitine deficiency.
ALCAR is especially helpful for those suffering from age-related cognitive decline. Studies show it helps stop or reverse brain degeneration with Alzheimer’s Disease, and geriatric depression. Particularly in the early stages of the disease.
I suggest starting with a dose of 500 mg ALCAR daily. ALCAR is a great compliment to a stack including any of the racetams. Take enough Alpha GPC or CDP-Choline to eliminate a racetam-induced headache. Then add 500 mg of ALCAR.
Some have found ALCAR stacked with Coenzyme Q-10 has a profound effect on everything from mood to bipolar disorder. Especially combined with Alpha-Lipoic Acid.|
You can also get 500 mg Acetyl L-Carnitine, 100 mg BioEnhanced™ R-Lipoic Acid, 100 mg CoQ10, 10 mg BioPQQ®, and 2.5 mg BioPerine® in one dose of my favorite energy supplement Click for Performance Lab® Energy .
Age-related cognitive disorders like Alzheimer’s may want to up the dose to 1,500 mg per day.






Join The Discussion - 372 comments
Jamie Kurtis
November 25, 2025
Hey David, I used to use ALCAR but I notice the effects diminish after a week at first. And nowadays, I notice after a day or two of ALCAR 500mg once a day working well, the following days firmly are bad fatigue, slight depression, and a little bit of brain fog while having an anxiety increase. I tolerate cdp choline greatly, but why is ALCAR, which is one of my favorite supplements, such a short lived product for me?
David Tomen
November 27, 2025
Jamie, you may be hypthyroid and not even know it. Tens of thousands of people just in the USA are hypo because their doctors do not know how to read thyroid hormone labs. They look at TSH only which tells you nothing. Read the last paragraph above in the “Side Effcts” section.
I suggest you find someone who will run a full thyroid lab for you including Free T4, Free T3, Reverse T3, and the two antibodies that can indicate Hashimotos. Learn how to read your own thyroid labs too so you’ll know if the doc who ordered the labs knows what she it talking about. Learn that here: https://stopthethyroidmadness.com/lab-values/
Samson Hinds
January 30, 2025
Will Alcar, bacopa (cognance), and CDP choline be effective for cognitive function, memory and alertness, as well as energy and motivation throughout the day? all of these long term
should i switch AlCAR to rhodiola?
thanks!
David Tomen
January 31, 2025
Samson, to increase acetylcholine for alertness and memory you need CDP-Choline and ALCAR together along with Vitamin B1 & B5, magnesium and Vitamin D3.
Marcie Webber
December 28, 2024
Is ALCAR safe for long term use? Does it need recycling?
Thank you in advance Dave for your generosity of helping us.
David Tomen
December 30, 2024
Marcie, I’ve been using 500 mg ALCAR 2 or 3-times day for about 17 years. So, I’d say it’s safe to use long-term. And no, there is no need to cycle it.
Jeff S
December 11, 2025
Dave, have you seen the recent studies about ALCAR increasing TMAO up to ten fold? Any concerns with this?
David Tomen
December 11, 2025
Jeff, I have not. Would you please link to an official study and not someone’s blog showing this?
Jeff
December 12, 2025
Dave,
Here are the ones referenced on the reddit posts where people have been talking about it in nootropic subs for the past week:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/41243468/
https://www.explorationpub.com/Journals/ec/Article/101250
https://www.sciencedirect.com:5037/science/article/pii/S0021915015301921
One of the top sub posters actually had his blood TMAO checked after reading studies. He was a big ALCAR advocate. His bloods showed TMAO through the roof despite taking supplements that supposedly help mitigate it like PQQ, garlic, fish oil etc.
David Tomen
December 15, 2025
Jeff, there is this big scare about rising TMAO levels but so far I have not been able to find any solid evidence that TMAO is a problem. First, it is measured in urine which means it has already left your body at that point.
And then I see this statement by the author of a very throrough explanation of the implications of TMAO, choline and carnitine, “In the light of all this evidence, currently it is not totally agreed that TMAO by itself is a proatherogenic compound or just a biomarker of CVD.” (https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/10/10/1398).
And if someone is still freaked out by TMAO, apparently you can get rid of it by eating pistachios (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28432876/).
Jeff Stoutenger
December 15, 2025
Thanks for the reply! Always like some additional insight especially on scientific literature. Big fan of your website it has been absolutely pivotal to my transition off of adderall. I always had an immense interest in the subject of nootropics and biohacking in general so I think it is so awesome that you have built this terrific platform for others like me to continue to learn and grow their brains. Keep up the good work!
Also side note: do you have any plans to do a write up on bromantane? It really helped me recover from adderall. I think it is really an amazing compound. Just curious. Thanks again!
David Tomen
December 15, 2025
Thank you Jeff. Bromantane is on my “to do” list. Which is a very long list so stay tuned!
Julie Gilbert
August 3, 2024
Hi David, I am 66F and tried ALCAR 500mg and became extremely tired, foggy headed and sort of depressed. I did not combine with any other supplement, took away from food. I will say I had a similar reaction to Taurine–I obviously do not know if its in any way related, but thought I would mention it. My reasons for trying the ALCAR was both for nerve pain relief and the cognitive benefits, but the latter for sure was a fail. Any idea why I would get such a paradoxical reaction?
David Tomen
August 6, 2024
Julie, there is no “one pill” solution for optimizing your brain and body. See this article for what has helped thousands of people in your age group: https://nootropicsexpert.com/best-nootropics-for-the-aging-brain/
Maurice
June 26, 2024
Hello David.
I would like to take ALCAR in combination with Citicoline and L-Tyrosine. Is that possible or will I then have the problem that these three amino acids interfere with each other’s absorption?
Thank you very much!
David Tomen
June 26, 2024
That is the best combo to increase acetylcholine and dopamine. And makes one of the most basic nootropic stacks. I’ve been using that combo every day for the last 17 years.
Maurice
June 26, 2024
Thank you David for your answer. A quick additional question: I also take Arginine and Pine Bark Extract daily. Can I also take these two together with the amino acids mentioned (tyrosine, alcar, citicoline) or should I wait a little in between?
David Tomen
July 2, 2024
Maurice, you take take them at the same time. Just remember that you need two doses during the day of Tyrosine, Citicoline and ALCAR.