Table of Contents
DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) is an omega-3 fatty acid. DHA is crucial for the healthy structure and function of your brain at all ages.
DHA impacts your brain’s signaling systems, neurotransmitters, memory, learning, focus and attention. It helps reduce and even repair cognitive decline.
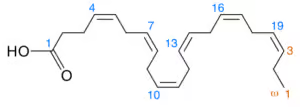
The best algae-sourced DHA on the market today is Performance Lab® Omega-3 which contains 600 mg of DHA and 300 mg of EPA per dose.
The famous Framingham Heart Study followed-up with 899 men and women who were free of dementia. Subjects had a median age of 76 years. And were followed for 9.1 years for the development of dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease.
Results from the study showed 99 new cases of dementia including 71 of Alzheimer’s. The researchers concluded that those with the highest levels of DHA were “associated with a significant 47% reduction in the risk of developing all-cause dementia”.[i]
DHA helps:
- BDNF. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is your brain’s growth hormone. DHA has the ability to turn on your brain’s BDNF.
- Neuroplasticity. DHA helps your brain build new neural pathways. Critical for maintaining a healthy brain. And optimizing neural signaling and cognition.
- Neuroprotection. DHA acts as an anti-inflammatory by reducing the enzyme COX-2. Inflammation is a key factor in both Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease. And in every other neurodegenerative disease.
What is DHA?
DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) is an omega-3 fatty acid. Your brain is made up of 60% fat. And much of that fat is DHA.
Your body does not make DHA on its own. So you must get it from food or a supplement. And if you are a vegan, you are at serious risk of a life-threatening DHA deficiency.
Foods that are rich in DHA include fish, fish oil, Krill and other crustaceans, and algae.
But fish do not make DHA. Fish and other marine predators get it from smaller fish and crustaceans that feed on algae. It’s algae that has the enzymes to produce DHA that we need to remain healthy.
The best algae-sourced DHA on the market today is Performance Lab® Omega-3 which contains 600 mg of DHA and 300 mg of EPA per dose.
DHA from eggs and some dairy products only supply about 20 mg of DHA per day.
DHA is essential for maintaining brain health, memory and learning functions. DHA reduces brain inflammation, stimulates new nerve cell growth, and assists in brain cell repair.
How does DHA Work in the Brain?
Your brain is composed of 60% fat. 15 – 20% of your cerebral cortex is DHA. Even the retina in your eyes is 30 – 60% DHA. Making DHA the most essential nutrient for eye and brain health.
The highest levels of DHA are found in phosphatidylserine (PS) and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE).[ii] Lower levels are found in phosphatidylcholine (PC).
PS makes up about 70% of neuron tissue mass. It helps in the storage, release and activity of neurotransmitters and receptors.
PC also makes up part of the neuron tissue mass. And helps in maintaining cell structure, fat metabolism, neuron signaling and the activation of a number of enzymes.
And PE is part of neuron cell membranes. PE is involved in cellular signaling.
PS, PE and PC are called phospholipids. Together they alter the fluidity of cell membranes. Changing the fluidity of cell membranes alters their permeability and protein activity. And influences cellular signaling.
Made up largely of DHA, these cellular membranes regulate entry into the cell, and control neuroreceptor function. Which facilitates cellular communication between, and within cells.
DHA also reduces inflammation by regulating proteins and enzymes within cells. And boosts the production of anti-inflammatory compounds that protect cells.
DHA maintains the activity of certain enzymes that control electrical signaling between cells. And it regulates the brain cell concentration of PS which is vital for cell survival.
And DHA regulates calcium oscillations, which are involved in neurotransmitter release, mitochondrial function, gene activation, oxidative stress and brain cell development and growth (BDNF).
DHA vs. EPA: What’s the Difference?
Most medical authorities and scientists agree that Omega-3 oils are important for good health. Omega-3s boost brain function, decrease inflammation, reduce the incidence of fatal heart attacks and strokes, help autoimmune diseases and improve vision.
 We have general agreement about the health benefits of Omega-3 oils. But few appreciate the difference between DHA (docosahexaeonic acid) and EPA (eico-sapentaenoic acid).
We have general agreement about the health benefits of Omega-3 oils. But few appreciate the difference between DHA (docosahexaeonic acid) and EPA (eico-sapentaenoic acid).
The ratio of DHA and EPA varies a lot in commercial Omega-3 supplements. Most have higher concentrations of EPA to DHA. Mainly because it’s cheaper to manufacture, and has less of a fishy odor.
But studies show that most of the brain health benefits of Omega-3’s are derived from DHA rather than EPA.
One study in Chicago followed 815 residents from 1993 – 2000. Study subjects were between 65 and 94 years. 131 study participants developed Alzheimer’s Disease. Those who ate fish at least once a week had a 60% less risk of Alzheimer’s compared to those who didn’t eat fish.
Researchers found that it was the intake of DHA rather than EPA that reduced the risk factor in getting Alzheimer’s. EPA made no difference whatsoever.[iii]
How Things Go Bad
From reviewing the “How does DHA Work in the Brain” section of this article, you can imagine that when things go bad with DHA – they go really bad.
Fish and marine oil supplements like krill oil are a source of DHA and EPA because they get it from algae. Plants contain another Omega-3 called alpha-linolenic acid (ALA).
Technically ALA can be converted to DHA and EPA. But most modern humans lack the ability to convert plant sources of Omega-3s into all the DHA our brain needs.
When we don’t get enough DHA, we experience:
↓ Problems with attention, learning and memory
↑ Depression, anxiety, aggression, anger, suicide risk
↑ Bipolar disorder, Alzheimer’s Disease and Schizophrenia
Not having adequate levels of DHA in the brain cause things to break down. If the inadequate intake of DHA goes on for a while, disease starts to set in. Including neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and cancer.
DHA benefits
DHA makes up much of the gray matter in your brain. It’s an integral part of cell membranes and their function.
Your brain is 60% fat. And a large part of that is DHA.
The good news is; degenerative conditions can not only be prevented by adding DHA to your nootropic stack. It can also be reversed.
In one study, researchers worked with 485 elderly subjects with memory problems. They saw significant improvement with those taking 900 mg of DHA per day for 24 weeks compared to the control group.[iv]
In another double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, scientists worked with 49 women aged 60 – 80 years. One group received 800 mg per day of DHA for 4 months.
Researchers found those using DHA had a significant improvement in verbal fluency scores. And an improvement in memory and learning.[v]
How does DHA feel?
Chances are when you start using DHA you won’t feel it. There’s no profound stimulant feeling.
But if you suffer from chronic depression, within a few weeks you should feel the depression lift.
After supplementing with DHA for a while your cognition will be better. You’ll think clearer and quicker. Your memory and ability to learn will improve. And you’ll likely have more energy and motivation.
But it is very likely you won’t think to attribute these improvements to adding DHA to your stack. Something else will get the credit.
DHA Clinical Research
DHA is crucial for an optimally functioning brain. The goal of every neurohacker. DHA impacts your brain’s structure, signaling systems, neurotransmitters, memory, learning, focus and attention.
We have decades of clinical research verifying the importance of DHA in your nootropic stack. And several books have been written on the subject in the last couple of years. Here’s just a snippet of what’s available…
DHA Reduces Hostility and Anger
In a study with 41 university students in Japan, scientists compared a high-DHA diet (1.5 grams/day) with placebo. This was recorded over 3 months to see the effects on hostile responses.
The researchers found a 27% incidence of hostile answers in the placebo group when nothing extraordinary was going on. And hostile responses rose to 92% during final exams.
There was no increase in hostility among those taking a DHA supplement. These guys even found DHA supplementation significantly reduced hostility among university staff.[vi]
DHA Restores Neurotransmitters & Memory
As your brain ages, there is an increase in membrane rigidity. This causes changes in synapses resulting in a decrease in transmitter release. Long-term potentiation is affected which impairs the development of memories.
Several studies have shown that DHA can support healthy levels of these neurotransmitters. In one study with aged rats, researchers restored neurotransmitter release in the hippocampus. And reversed age-related memory problems.
Adding omega-3 fatty acids to the rat’s feed for 8 weeks raised concentrations of DHA in the rat’s brain. And actually reversed age-related memory impairment.[vii]
DHA Improves Attention & Learning
DHA also has an effect on neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, acetylcholine, glutamate and dopamine. Deficiencies in DHA have been shown to lower levels of dopamine. Resulting in problems with attention and learning.[viii]
DHA even plays a role in neurotransmitter receptor function. DHA affects brain cell membrane structures including neuroreceptors.[ix]
Some of these receptors communicate inside cells when stimulated by glutamate, serotonin and acetylcholine.[x] The numbers of these receptors can be increased by you, by adding DHA to your nootropic stack.
So if you are using nootropics that affect things like acetylcholine, serotonin, dopamine and serotonin in your brain. It would be wise to add DHA to your nootropic stack. And ensure you get the most bang for your investment in nootropics.
DHA Recommended Dosage
Recommended daily dosage of DHA is 1,000 mg.
Fish oil supplements vary in ratios of DHA to EPA. Salmon naturally contain more DHA than EPA. A supplement from algae may contain only DHA.
Krill oil provides both DHA and EPA. So read the labels. And whatever supplement you get, make sure you end up with at least 1,000 mg of DHA.
And recall that fish and krill do not produce DHA on their own. Marine life get their DHA from algae in the wild.
Most brands of fish oil have been proven safe, and free of mercury. And do not contain unsafe levels of PCB’s (polychlorinated biphenyls).
To further avoid the contaminants in an unrefined supplement, choose a fish oil or Omega-3 supplement made from small, oily fish like anchovies, sardines or menhaden. And check the labels carefully for purity.
Ideally, get one of a few supplements now available that are pure, refined DHA. With lower or minimal amounts of EPA.
DHA Side Effects
Fish oil capsules commonly have both DHA and EPA. Capsules with EPA are not recommended for infants or small children. Because they upset the balance between DHA and EPA during early development. This also applies to pregnant women.
Fish oil could cause minor side effects like loose stools, upset stomach and belching.
Fish oil may lower blood pressure. So if you already take a medication to lower blood pressure, make sure you talk to your doctor first.
If you’re supplement contains EPA, it could interact with blood thinners and increase bleeding. Same is true for aspirin. But this is not true of DHA. DHA-only supplements do not thin the blood.
Fish oil supplements may lower blood sugar levels. So be careful if you’re on diabetes medications.
Omega-3 fatty acids may reduce some of the side effects of cyclosporine which is used to stop rejection after an organ transplant.
Type of DHA to Buy
 DHA is available as a supplement in two forms:
DHA is available as a supplement in two forms:
- Fish oil or Omega-3 capsules. Which usually have both DHA and EPA. Most Omega-3 supplements contain higher amounts of EPA compared to DHA. But for our purposes, and to support cognitive health, we need an Omega-3 supplement containing higher amounts of DHA to EPA.
- DHA from fish oil. Some supplement manufacturers now offer capsules containing higher amounts of pure, refined DHA. And reduced amounts of EPA. Our brains require 1,000 mg DHA per day. So look for a DHA supplement that provides 1,000 mg DHA in 2-3 gelcaps.
- DHA from algae. Which may or may not contain EPA and is vegetarian friendly. Algae is the natural source of these Omega-3s in the wild and where fish and other marine life get their Omega-3s.
For as little as $49/month you can experience better cognition, memory and mood simply by using a daily DHA supplement. My favorite is Click for Performance Lab® Omega-3 which contains 600 mg of DHA and 300 mg of EPA per dose.
Performance Lab® Omega-3 contains life’s™ OMEGA algae oil which supplies natural triglyceride Omega-3s that are 70% more bioavailable than synthetic ethyl esters used in cheaper and lower quality Omega-3 fish oil supplements.
Performance Lab® Omega-3 is delivered in NutriGels which are vegan, carrageenan-free softgels. No fishy smell or aftertaste and easy on your digestive system.
Try a bottle today: Click for Performance Lab® Omega-3
Nootropics Expert Recommendation
DHA (Omega-3) 1,000 mg per day.
 I recommend using DHA as a nootropic supplement.
I recommend using DHA as a nootropic supplement.
Your body does not make DHA on its own. So you must get it from food. Or take it as a supplement.
DHA is one of the most important nootropics you can add to your stack. Your brain is 60% fat. And much of that fat is DHA.
DHA is critical for brain cell repair and regeneration (neurogenesis). And it is an integral part of neural signaling. Both between neurons as well as inside brain cells.
DHA has an effect on critical neurotransmitters and neuroreceptors. It is a powerful anti-inflammatory. And is involved in neuroplasticity.
Hundreds of studies on Omega-3s and DHA show benefits in preventing and even reversing neurodegenerative disease.
It’s best if you find a supplement that contains twice as much DHA than EPA. Such as Click for Performance Lab® Omega-3 And you can safely take 1,000 mg of DHA per day.








Join The Discussion - 229 comments
Laura
March 31, 2020
Hello David,
Is Cod Liver Oil a good supplement for DHA and EPA ??
I am trying to get a supplement for Vit D, A, DHA and EPA.
Thank you.
David Tomen
March 31, 2020
Laura, not if you’re looking to improve brain health. For that you need 1,000 mg per day of DHA and need to use a high quality, pure DHA supplement.
For best results quit looking for a combination and use three supplements at the exact dosage you need to achieve your goals.
Mr.EPA
March 9, 2020
Hi David,
I have a concern about ratio between DHA and EPA.
I have read that high rate of EPA can impact the cell membranes and to be in healthy status the dosage for DHA needs to be higher than EPA in 10:1 ratio or at least 10:5 ratio.
I do respect these claims but practically I see no evidence.
because I see some people get benefits from higher EPA for cardio which leads to benefits the brain indirectly because more healthy heart can lead to more healthy brain.
I have more than two years using DHA in higher doses, 1500DHA mg and 200mg EPA.
I am thinking if I can increase the EPA to be 1000mg or even 2000mg, and based on experimenting if my body accepts this change without side effects? then I will be considered I get more healthy benefits form this step.
Please advise about this step, how do you see it, and if succeeded with the point that higher EPA can have indirect benefits to the mind and overall health without interfering with the DHA dose.
This is my consern and thanks for listening.
appreciated your valued opinion.
Thanks & Regards
David Tomen
March 9, 2020
I have provided links throughout this review to clinical studies showing why DHA is critical especially for brain health. It’s true that your body requires some EPA. But far lower doses than normally found in Omega-3 supplements.
Have you seen this part of this review? https://nootropicsexpert.com/dha/#dha-vs-epa-whats-the-difference. I’ve seen zero evidence that more than a couple hundred milligrams of EPA to be helpful.
Mick
February 17, 2020
Hi David, I would like to try Blackmores Omega Brain Fish Oil.
Concentrated Omega – 3 Triglycerides – Fish 1g (1000mg) containing Omega – 3 Marine Triglycerides 600mg as:
EPA- 100mg
DHA-500mg
Dosage: 1 capsule twice a day.
Is this the right Fish Oil to take?
And if it is, what is the best time to take it?
Should I take one capsule in the morning and one before bed?
Thanks.
David Tomen
February 18, 2020
Mick, I’m not familiar with the manufacturer so will leave it to you to figure out if it’s a quality supplement. This post will help with that part: https://nootropicsexpert.com/7-tips-for-choosing-the-highest-quality-nootropic-supplements/
Your brain needs 1,000 mg per day of DHA. So double what the manufacturer suggests of that supplement. Best to take it in the morning because DHA can be energizing.
Mick
February 19, 2020
Thanks David
Stevie
January 21, 2020
I’m confused about the ratio of EPA to DHA. The link above indicates the opposite recommendation from what has been suggested in your article.
I’ve also read that EPA is energizing while DHA is calming. Are you familiar with this claim?
David Tomen
January 22, 2020
Stevie, I removed the link to the website you pointed to but did take a look at the 3 studies the author referenced. The first 2 studies were for Omega-3 levels in children diagnosed ADHD. No idea why they included the 3rd one.
The first study concluded that kids with ADHD typically tested for insufficient levels of Omega-3 but the authors could not decide if supplementation was a good idea.
The 2nd study was an analysis of dozens of studies with ADHD kids. The authors of that study concluded there was not much evidence that supplementation of Omega-3s helped these kids. Most of the studies focused on DHA. But the authors thought there may be enough evidence in favor of a slightly higher EPA/DHA ratio to help children with ADHD.
It appears that the author of the site you pointed pulled her claims of high EPA to DHA out of thin air before making her recommendations. I see a lot of that …
My entire focus on DHA in this review was using Omega-3s in adults. And each study I looked at was in favor of higher DHA supplementation. I couldn’t find any evidence showing benefit using EPA for adults and the brain.
Since I’ve written this review I’ve found a couple of DHA supplements with a high DHA/EPA ratio that work. I know because I’ve tested them.
It’s true that you do require some EPA. But we have overwhelming evidence in adults that most are low in DHA and suffering because of it.
I’ll be updating this review recommending a DHA supplement with much smaller amounts of EPA included. And not pure DHA as I’ve done in the past.
Dan
December 4, 2019
Hello,
I weigh 300 pounds. Would I need to take more than 1,000 mg of DHA because of my weight?
Thanks,
Dan
David Tomen
December 4, 2019
Dan, nobody has ever asked me a question like that before.
I have no evidence of this but I’m pretty sure the answer is “NO, you do not require more DHA because of your weight”.
And it’s because you may weigh more than the person next to you. But your brains weight about the same. And would require the same amount of DHA daily as any human adult on the planet.
Shawn
October 11, 2019
What are you thoughts on calamari derived dha? Is that better than algae dha or about the same? Also I know you said epa thins the blood but would 50mg of epa included with calamari dha thin the blood? I’ll like to combine it with Gingko Biloba. (60mg)
David Tomen
October 14, 2019
Shawn, recent studies show the bioavailability in phospholipid form of DHA from Algae vs. Calamari is about the same: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25360534.
I would think any amount of EPA is going to thin the blood but I have no proof. So if you’re going into surgery or worried about blood thinning for some other reason I’d avoid supplementing with any kind of Omega-3.
Gregory Anderson
October 10, 2019
What most DHA you can take per day?
David Tomen
October 11, 2019
Gregory, the recommended dosage of DHA is 1,000 mg per day. One study in Japan used 1,500 mg with some success. A couple of other studies with elderly people used 800 and 900 mg of DHA for several weeks which showed significant improvement in verbal fluency scores, memory and learning.
Sara
September 23, 2019
Hey David,
I’ve just started taking DHA Capsules (DEVA Vegan Omega-3 DHA delayed release from algae). If I’m reading it right it says it contains Microalgae Oil (40%) DHA which typically provides DHA 200mg.
I watched your video which suggests 1000mg. Could you please recommend a vegan suppliment that is 1000mg? I’m having a really hard time finding what would be idea and as I have recently become pregnant I really want to provide the best nutrients etc that I can for myself and the baby.
Lots of love from Australia!
David Tomen
September 23, 2019
Sara, the best DHA supplements I’ve found so far that provide 1,000 mg DHA in two capsules are by Nature’s Way and NOW Foods: https://amzn.to/2m77Rk6 or https://amzn.to/2m9n04n