Table of Contents
The Definitive Guide to Nootropics
Nootropics can help increase your memory, boost learning ability, improve your mood and assist overall brain function. If you’re new to nootropics, or wonder about the difference between a nootropic and a smart drug, then this page is for you.
Here you’ll find the definition of a nootropic, how to pronounce the word “nootropic”, the origin of the word nootropic, other names or synonyms you’ll come across when referring to nootropics, a brief explanation of nootropic ‘stacks’, if they really work, how they work and what nootropics can do for you.
You’ll also find information on nootropic safety. And if they have any side effects. Use this guide as a primer to clear any confusion, and get started safely with nootropics.
In just a few minutes you’ll have a better understanding of each topic. And links through to pages in more detail when an in-depth explanation is needed.
You can even click each of the titles in the Table of Contents and go directly to that section if you’re pressed for time.
What are Nootropics?
Nootropics are a class of substances that improve brain function. Also referred to as neuro-enhancers, cognitive boosters, or memory enhancers. Nootropics can be natural or synthetic.
Experienced bio-hackers often make a distinction between nootropics and smart drugs. For our discussion and to help you understand what they are and how they’re used, we’ll cover the latest in nootropics research.
Nootropics are used to improve focus, motivation, memory, mood, and cognition. Each of these depend on different processes in your brain. And different substances can be used to affect each of these functions.
This idea of altering brain function is not new. Our ancestors were using herbs and alcohol to alter brain function for the last few thousand years.
Origin of the word ‘Nootropic’
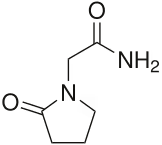
The term “nootropic” is relatively new. Romanian psychologist and chemist Dr. Corneliu Giurgea synthesized Piracetam in 1963. And coined the term “nootropic” in 1972.[i] It is derived from the Greek nous (“mind”) and trepein (to bend).
Definition of Nootropic
Dr. Giurgea gave us a list of five criteria that a substance must have to be considered a ‘true’ nootropic.
A true nootropic:
- Enhances memory and the ability to learn
- Assists brain function under disruptive conditions such as lack of oxygen and electroconvulsive shock
- Protects the brain from chemical and physical toxins like anticholinergic drugs and barbiturates
- Increases natural cognitive processes
- Must be non-toxic to humans, nor stimulate or depress the brain
Most of the time, when you hear the term ‘nootropic’ used, people loosely mean “cognitive enhancer”. A substance or compound that improves memory, increases cognitive processing speed, boosts alertness, concentration and focus, or a combination of these qualities.
At Nootropics Expert, I do my best to stick to the original definition of nootropic. And when a substance or compound strays from this strict definition, I’ll tell you the reasons why. And things to avoid when choosing a nootropic supplement.
How to Pronounce the word “Nootropic”
The formal or ‘correct’ way to pronounce the word “nootropic” according to dictionaries, encyclopedias, and a few in the nootropic community is:
nō-ə-ˈtrō-pik
Which sounds a little like ‘Noah’ as in the biblical Noah. And ‘tropic’ with the ‘tro’ rhyming with ‘go’.
However, most in the nootropic community pronounce the word ‘new-tropic’. With ‘tropic’ rhyming with ‘living in the tropics’ (which I did for many years).
There is no absolute ‘correct’ way to pronounce nootropic in my opinion. And anyone who takes issue with the pronunciation of the word likely needs an extra dose of Phenylethylamine. Or 30-minutes of meditation. Just to calm down and get on with building their stack.
Nootropic Synonyms
With the rapidly growing popularity of nootropics and other cognitive enhancers, you will come across many terms generally referring to the same thing. And it can get confusing especially for someone new to nootropics.
Nootropics are commonly referred to as smart drugs, brain drugs, memory enhancers, neuro-enhancers, cognitive enhancers, intelligence enhancers, racetams, nootropic supplements, brain supplements, neuroceuticals, nutraceuticals, and cognition-enhancing supplements.
Most experienced neurohackers simply refer to them as “nootropics”. And here at Nootropics Expert, I make the distinction between a “nootropic” and a “smart drug”.
Natural vs. Synthetic Nootropics
You can boost brain power in a variety of ways. Your end goal will often dictate if you should use a natural or synthetic nootropic. Let’s illustrate this with some examples.
First we’ll look at a synthetic nootropic, and then we’ll look at a natural nootropic. These are only two of dozens of nootropics in each category.
Dr. Giurgea’s piracetam is a cyclic derivative of GABA. GABA is naturally produced by your body. (But because it is not “natural”, piracetam cannot be sold in the USA as a “dietary supplement”. And since piracetam is not approved by the FDA for medical use, it also cannot be sold as a drug.)
Piracetam has been shown to support memory[ii], learning capacity, reduce mental fatigue, and improve concentration. It is sold as the prescription drug “Nootropil” in many European countries.
Clinical trials with piracetam have shown it may help your brain in several ways. Including increasing the effectiveness of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.[iii]
Acetylcholine is a chemical messenger that allows neurons to communicate with each other. It is vital for memory, focus, concentration and mental alertness. But piracetam is not the only way to boost acetylcholine function in your brain.
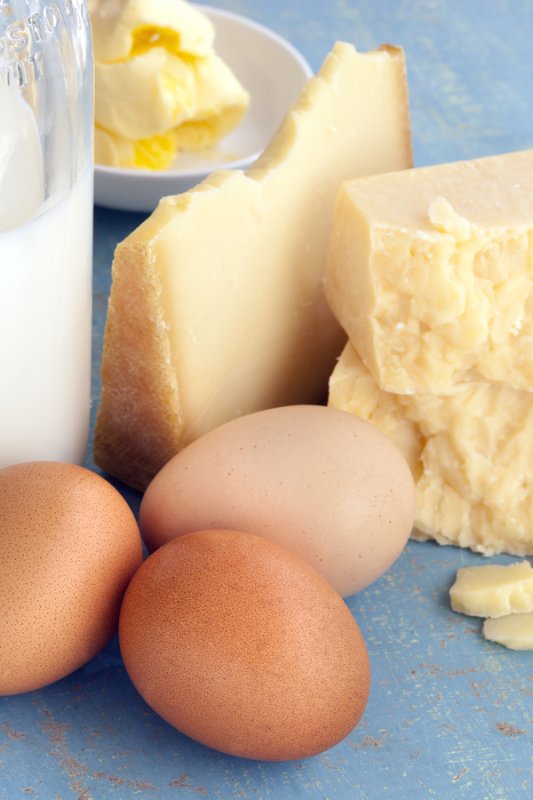
Your body naturally makes acetylcholine from healthy fats in your diet. Good sources of choline – the precursor to acetylcholine – include:
| Milk | Cheese | Eggs | Soy Lecithin |
| Fatty fish | Beef (esp. liver) | Almonds | Cauliflower |
| Pistachios | Spinach | Wheat germ | spirulina |
 You can also use supplements like Alpha GPC, CDP Choline, and choline citrate to boost choline.
You can also use supplements like Alpha GPC, CDP Choline, and choline citrate to boost choline.
So there is no best source for nootropics. Natural and synthetics work. Some work better than others. And everybody’s body really is different. It often depends what you’re trying to achieve.
 Do Nootropics Really Work?
Do Nootropics Really Work?
There is no question nootropics work. But opinions vary across the board how well they work. Decades of clinical studies and nootropic user comments and reviews show improvement in many areas. It depends on the person and the specific nootropic.
Personally, I was able to get off of ADHD meds (Ritalin) for a year. And manage my condition just as well with nootropics.
Many university students will tell you their high grades are directly related to a stack like aniracetam, Pramiracetam, ALCAR, L-Theanine and caffeine.
Users report the ability to:
- Interpret and retain complex information
- Learning is faster and more efficient
- Signal to noise ratio gets better
- Emotions are affected generally in a positive way
- Anxiety levels drop
- Sociability can be affected either way.
In the Nootropic community the big proviso is always “your mileage may vary”. Dosage can influence the desired (and undesired) effects of many nootropics. With some of the newer nootropics (smart drugs in particular) the jury is still out on how well, or even if they work.
This includes stacks put out by companies who either don’t disclose individual dosage of each ingredient. Or companies who have poor quality control over, and amount of the ingredients used in a capsule.
The underlying lesson is research and experimentation. Read what others say and research clinical trials. But always remember more is definitely not better.
For an in-depth dive into how nootropics work including influencing brain energy, signaling, cell health & repair, cerebral blood flow, brain waves and fatigue, see my post on:
What is the Best Nootropic?
It depends on what you mean by “best”. And maybe not the answer you’re looking for. But we have a lot of variables in play here. And especially for someone new to nootropics, this is what you need to consider…
If you are a university student, an entrepreneur, a business executive, a stay-at-home mom or dad or a senior – what are you trying to improve?
By using nootropics, you can benefit from improved memory, focus, learning, mood or motivation. Some even have anti-aging benefits. You have several options for each benefit you’re trying to boost or correct.
Here are the…
Best Nootropics for Learning & Memory
Best Nootropics for Depression
Hacking Motivation with Nootropics
Hack Your Flow State with Nootropics
But to be perfectly honest with you, from my personal experience, one nootropic to boost memory may work better for you and not as well for me.
As a general rule, we’re all the same. And generally one nootropic will work better for focus for most people. But I have found each nootropic can have a different effect at different doses on different people.
Each one of us has variations in cognitive “wiring”. Our chemical and genetic makeup is different. We’re influenced by the foods we eat, where we live, the air we breathe and the genes we inherited from our parents.
Science hasn’t yet developed the “magic pill” to solve all cognitive issues. It’s why we experiment, read reviews, and listen to other neurohackers. There is no one-pill solution!
It’s why I created and continue to develop Nootropics Expert®. To help you in your journey in creating the perfect nootropic stack for you at this time in your life.
Learn How to Create the Best Nootropic Stack for You here.
Best Nootropic Stack for Beginners
If you are new to nootropics, and don’t know where to start, here’s a few things to keep in mind.
Each nootropic supplement has a unique mechanism of action in your brain. As soon as you add just one more nootropic, it may have some impact on how the first nootropic works in your brain.
Sometimes this combination of two or more nootropics is intentional. For example, Piracetam boosts the sensitivity of acetylcholine receptors in your brain. Which causes your brain to demand more acetylcholine to satisfy this demand.
Experienced neurohackers have learned that ‘stacking’ Piracetam with a choline supplement like Alpha GPC or CDP-Choline boosts the effectiveness of Piracetam. With even more focus, learning and memory improvements.
But sometimes the interaction between two or more nootropics taken together is unintentional. And could cause adverse side effects like depression, irritability or insomnia.
Huperzine-A is a classic example because it acts as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor which means it boosts levels of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in your brain.
So if you add Huperzine-A to your stack, you may want to reduce your dose of a choline supplement like Alpha GPC or CDP-Choline. Or you could experience the side effects of too much acetylcholine.
You’ll also want to keep in mind that some nootropics have a cumulative effect in your brain. They ‘build-up’ over time. Especially if you take them everyday. Take Huperzine-A for example which has a half-life of 10 – 12 hours. If you took Hup-A every day, your body wouldn’t have the chance to flush the old Huperzine-A out of our system before you took your next dose.
Some nootropics are water-soluble while some are fat-soluble. What does this mean?
To help you if you’re just getting started in nootropics and building your first stack, check out this article on:
Beginners Guide to Nootropic Stacks
The guide will take you through building a nootropic stack step-by-step. And show you how to avoid the many pitfalls and mistakes many new neurohackers make when first getting started with nootropics.
How do Nootropics Work?
Nootropics can affect your brain by influencing brain waves, cerebral blood flow, cellular energy, hormones, neurotransmitters, neuroplasticity or growth factors.
Dozens of natural and synthetic substances have nootropic properties. Each can affect one or more of several categories affecting your brain. Nootropics work by affecting:
- Brain energy
- Brain cell signaling
- Brain cell health & longevity
- Brain blood supply
- Brain Waves
- Brain fatigue
- Brain repair
For a detailed overview of each of these categories, go to my post called:
You’ll find how each affects your brain, what can go wrong, and examples of nootropics that can address each issue.
You can also get detailed explanations of dozens of nootropics here on Nootropics Expert. Each article explains what the nootropic is and where it came from, mechanisms of action on how it works in your brain, why you may want to add it to your nootropic stack, dosage recommendations, forms each nootropic comes in, references to dozens of clinical studies, and where to buy the supplement.
Visit the “List of Nootropics” page and scroll through the Table of Contents. Each nootropic summary on that page links to a detailed article on that nootropic and how it works.
What Can Nootropics Do for Me?
 Referring to a section near the beginning of this article, the right nootropics can help you:
Referring to a section near the beginning of this article, the right nootropics can help you:
- Interpret and retain complex information
- Learning is faster and more efficient
- Signal to noise ratio gets better
- Emotions are affected generally in a positive way
- Anxiety levels drop
- Sociability can be affected either way
Nootropics may also help to repair years of damage to your brain, and possibly find a healthier alternative to ADHD meds.
For more on ADHD and ADD, check out my post on:
Best Nootropics for ADHD & ADD
For athletes or anyone maintaining a serious exercise regimen some nootropics can help up your game. And give your body and brain the fuel it needs to operate at your peak.
Hack Motivation with Nootropics
Hack Your Flow State with Nootropics
Best Nootropics for Learning & Memory
Best Nootropics for Depression
Need more energy to power through your day? Mitochondria are where your body’s energy is produced. Allowing you to hear, feel and see. Mitochondria beat your heart, stimulate your sex drive and allow you to think.
Your brain has a higher concentration of these little cellular powerplants than most other cells in your body. You can have several thousand mitochondria in each brain cell. They even have their own DNA.
You can hack your mitochondria with nootropics. Learn how here:
Hack Your Mitochondria with Nootropics
If you are dealing with anxiety or depression and conventional prescription anti-anxiety meds, or antidepressants just aren’t helping…
Check this… are you also battling with abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, or diarrhea? Your brain fog, anxiety or depression could be a gut problem. Recent research has established a strong gut-brain connection.
And when you address gastrointestinal issues, you’ll often find that depression, anxiety and brain fog are gone too. Learn how here…
Psychobiotics: The Gut-Brain Connection
Are Nootropics Addictive?
A true nootropic as defined here (a natural method of boosting brain performance), are safe and generally non-addictive. Some nootropics can give you long-term benefits even after you stop using them.
Smart drugs which are typically pharmaceuticals can be addictive. Particularly those acting as stimulants.
Nootropics generally have very few side effects, are non-toxic when taken at recommended doses, and do not cause withdrawal symptoms once you stop using them.
To learn more about nootropics vs smart drugs, tolerance, psychological addiction, nootropics and withdrawal, and non-addictive alternatives to smart drugs, see my extended article on:
Nootropics vs. Smart Drugs — What’s the Difference?
Smart Drugs are not the same as nootropics even though some may have similar benefits.
A smart drug is typically a prescription pharmaceutical used to treat the symptoms of ADHD or narcolepsy. They are central nervous system stimulant drugs. And the most commonly prescribed are Adderall (dextroamphetamine) or Ritalin (methylphenidate).
These stimulants help with focus and energy in someone who is truly clinically ADHD. They produce spikes in dopamine and norepinephrine.
Adderall, Ritalin and other stimulants are very powerful drugs. And can include side effects such as decreased appetite, irritability, mood swings, anxiety, sleep problems, and cardiac issues. Dependency and addiction is a growing problem with their use.
Two other smart drugs of note are Modafinil and Adrafinil. These are wake-promoting agents that have a different chemical make-up from stimulants like Ritalin and Adderall. But exhibit similar side effects in many people.[xii]
Nootropics are described as having the characteristics of enhancing learning and memory. It should protect the brain while increasing natural cognitive processes. And should not be toxic, nor stimulate or depress the brain.
You could think of a nootropic as food for the brain, while a smart drug is exactly that — a drug for the brain.
Let’s be clear.
Smart drugs can kill you. And
nootropics can heal your brain.
For more on the “dark side” of smart drugs including more detail on methylphenidate (Ritalin), Adderall, modafinil, and prescription ampakines, see my post on:
Smart Drugs – The Bad and the Ugly
Nootropic Safety & Side Effects
One of the qualifications to be called a nootropic is they must be extremely safe, and non-toxic to humans. This from the original definition by Dr. Giurgea who invented piracetam.
For this reason, “smart drugs” like Ritalin and Adderall do not qualify as a nootropic.
Most nootropics have few, if any, drug interactions. And should not complicate existing health conditions.
But a strong word of caution here… carefully read the dosage recommendations and side effects for each nootropic you’re considering adding to your stack. Every article for each nootropic listed here on Nootropics Expert® goes into detail on what to look out for. Including possible drug interactions.
So care must be taken with anything that alters dopamine or serotonin in your brain. Particularly if you are on any kind of SSRI, MAOI, or other anti-depressant medication.
Nootropics are generally made from plants, or made up of ingredients from plants. Or are purified components or extracts of plants.
The racetam-family of nootropics are derivatives of chemicals naturally produced by your body. For example, piracetam is a cyclic derivative of GABA which is naturally produced throughout your body, including your brain.
Nootropics are generally safe if you use them as recommended. You don’t want to go overboard with Vitamin D, melatonin or zinc because it could cause problems. Likewise, follow directions on the label and get advice from experienced nootropic users.
Many clinical studies have been done on nootropics over the last 40 – 50 years establishing their safety. And no one who has used a nootropic at recommended doses has ever OD’d to my knowledge.
Some nootropics like the racetams can work as a precursor to, or increase the efficacy of acetylcholine in your brain. In other words, they boost the uptake of choline.
So, for example the most commonly reported “side effect” of using racetams are headaches. And they usually occur in a specific part of your brain.
The best way to counteract a “racetam-headache” is to use a good source of supplemental choline such as Alpha GPC, CDP-Choline, or Cognizin®.
Read more about:
Nootropics Safety & Side Effects
Are Nootropics Legal?
In the USA, nootropics are generally classified as “dietary supplements” or “research compounds“. And can be purchased and used legally for personal consumption.
Smart drugs like Ritalin, Adderall, and Modafinil are prescription “drugs” and require a prescription from a licensed medical professional.
Some nootropics, particularly synthetics are classified as a prescription drug in some countries. For example, Citicoline, which is a supplement in the USA, qualifies as a prescription drug in much of Europe.
Piracetam and other racetam-class nootropics are only available by prescription in Russia, the United Kingdom and Australia. SAM-e is a prescription drug throughout Europe. And Vinpocetine, derived from the periwinkle plant is prescribed as a dementia drug in Japan and parts of Europe.
Dietary supplements are available in the USA without a prescription. And in many other countries. However, please check the status of any particular nootropic and their classification in your country.
See the page on the legal status of nootropics in your country here:
Are Nootropics Legal in My Country?
That page is updated as new information comes in from readers and neurohackers like you. So if you have information about your country that’s not yet listed, please leave a comment at the bottom of the Are Nootropics Legal in My Country page. That page is checked by hundreds of visitors every day. Your input is greatly appreciated.





Join The Discussion - 212 comments
Shaheen Nayfeh
March 29, 2023
Hi dr how are
Sorry my English isn’t that good
Before 6 month i was having big insomnia i cant sleep at all
But when i started to take
L theanine Around 400 mg
Tryptophan around 2 gm
Tyrosine around 2 gm
For the first time of my life these things helped me alot and i was feeling happy
but now it has been almost
2 month i cants sleep more than 2 hours
I always wake around 3-4 am and cant get back to sleep i cant work because of these 2 hour
,icant do anything at all
Plz help me im in Kuwait and here they don’t understand anything about these thing
Plz save my life
Ido believe now i have some kind of hormonal issue (idont know)
What test to do
David Tomen
March 29, 2023
Shaheen, I highly recommend that you learn exactly how each of the supplements you are using work in your brain. AND follow dosage recommendations including what time of the day to take them.
2 gm of L-Tyrosine is far above the standard adult dosage of 500 mg twice per day (morning and noon). 2 gm of L-Tryptophan is far above the standard adult dosage of 500 mg about 60 minutes before bed.
Please read at least one of my articles on nootropics for sleep like this one: https://nootropicsexpert.com/best-nootropics-for-sleep/
Kathleen Moore
March 11, 2023
Hello David. I was wondering if the magnolia bark is safe to take with lithium carbonate and Wellbutrin. I am actually interested more so for a sleep aid. Thank you much David
David Tomen
March 22, 2023
Kathleen see Magnolia Bark Side Effects here: https://nootropicsexpert.com/magnolia-bark/#magnolia-bark-side-effects. There is no mention of Lithium or Wellbutrin being contraindicated.
Dale George
March 10, 2023
Howdy David, how effective is NTFactor? I have had CFS for a long time. Now that I am turning 75, looking for a energy boost. What in your Nootropics list would you recommend? Thank you
David Tomen
March 22, 2023
Dale, NTFactor® is basically a multi with some low dose amino acids and looks to me to be absolutely useless.
If you are 75 then this is the article for you: https://nootropicsexpert.com/best-nootropics-for-the-aging-brain/. You need two supplements from each category in that article. Except the last one where you’ll need 5 different supplements to restore all your neurotransmitters.
If you could use further help with this please schedule a consultation with me.
Edward M Humphrey
February 8, 2023
David, I am 67 year old male who suffered a severe covid infection in December 2020. I was in hospital for 18 days. Six of those days were in ICU on vent. I know I am lucky to have walked out but I have suffered from covid long haul symptoms for over 2 years now. My worst symptom was brain fog in the beginning. That has seemed to improve slowly but the residual symptom that is not resolving over time is this sensation in my brain. I will describe it similar to “ringing in the ears” ,but this seems to be in my brain tissue. Its like the “brain zaps” ,but kind of low grade excitability ,constantly. Have you heard anything similar to this? Have you been able to advise on “covid brain fog”? I read where the SARS 2 virus particles where found in the brain upon autopsy of people who passed from this terrible virus. Thank you.
David Tomen
February 9, 2023
Edward, I have done several consultation with people with Long-COVID and am a scientific advisor on the board of the company working on a Long-COVID supplement. I suggest scheduling a consultation with me and I share what I know.
Brian Abercrombie
January 17, 2023
David, first thank you for the amazingly informative site.
I am 55 years old and retiring from teaching soon. I am planning on going into IT and will be taking the Comptia A+ certification exams in the next few months. I am going to need some nootropic help I am certain. I almost certainly have ADD, diagnosed as possibly tumefective MSbut never had brain mri(my daughter has it as well, my mother passed of Alzheimers so lots of worry about the brain. I also have pretty bad imposter syndrome as I have never paid for a test and failed it but I feel like the tests just weren’t hard enough.
I have a little experience with nootropics but am in no way particularly knowledgeable.
I am looking to work on focus, mood(combat depression and anxiety and imposter syndrome) brain fog, short term and long term retention, and procrastination.
Here are my thoughts: acetyl L carnitine(it has always helped me but I havent taken it in months) perhaps morning and lunch time, phenylpiracetam at lunch only on studying days,aniracetam morning and lunch, l-theanine in morning with coffee and some days at lunch with coffee, alpha-gpc. What others should be considered or should I replace some of these?Also is there enough fat in a glass of 2% milk for aniracetam absorbption?
David Tomen
January 18, 2023
Brian, you have enough time to get prepared for those exams if you get started right now.
Please read through this article carefully: https://nootropicsexpert.com/best-nootropics-for-the-aging-brain/. Choose one or two supplements from each category and follow dosing recommendations. But use every supplement suggested in the last section on neurotransmitters. That will make the most difference in the shortest possible time.
If you need more guidance then schedule a consultation with me. And I’ll help you put together a stack tailored specifically for you.
Dr Simon I Beshir, Cardiologist, Namibia
December 19, 2022
Hi David
Is there any experience, evidence for the use of Nootropics in children below the age of 5.
Theoretically, by providing nootropics to the developing brain, should boost the brain development, early learning and help to create “smart kids”.
Would you be able to provide any guidance.
David Tomen
December 21, 2022
Dr. Simon, good question. But everything I’ve seen so far in my research is it is dangerous to interfere or interrupt normal human brain development. The overwhelming consensus is that in gifted children it is present at birth and an inherited trait. It cannot be ‘created’ through nurturing.
Alan
December 10, 2022
Ok David,what about Agmatine Sulfate as a nootropic supplement? Have you every heard of it? I am taking it for nephropathy and it seems to help for that.
David Tomen
December 10, 2022
Alan, there is not nearly enough clinical evidence showing Agmatine Sulfate has any nootropic value. Which is the the criteria I use for researching, and writing about individual supplements.
Elliot
October 25, 2022
Hello and thank you for this amazing website.
Thanks to your reviews I bought the MindlabPro, the preworkout and the Sleep.
I have been taking them for a week now and the results so far are good.
Would you add any more nootropics to maximize the effects of Mindlapro?
Thank you very much
David Tomen
October 26, 2022
Elliot, it depends on what you are trying to do. I find one of the ingredients in Mind Lab Pro (NALT) is not dosed high enough for Adult ADD and I add another 500 mg L-Tyrosine when I use it.
And because some of the ingredients help produce dopamine, norepinephrine and acetylcholine you also need Vitamin D and magnesium.