Table of Contents
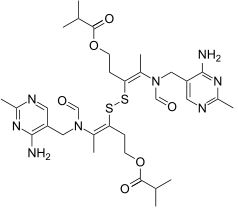
Sulbutiamine (isobutyryl thiamine disulfide) is a synthetic derivative of Vitamin B1 (thiamine). Thiamine was the first B Vitamin to be discovered by researchers. That’s why it’s called B1.
Sulbutiamine is simply two vitamin B1 molecules joined together. This chemical bond helps thiamine more easily cross the blood-brain barrier.
Japanese scientists first synthesized Sulbutiamine in an attempt to quell a health crisis within the Japanese population. After WWII, the Japanese diet largely consisted of rice. This left them deficient in several key nutrients including thiamine.
Insufficient thiamine led to a central nervous system disorder called Beriberi. But supplementing with thiamine alone didn’t help. Because of its poor bioavailability. And a lot of thiamine was needed to cure Beriberi symptoms.
Sulbutiamine is far more bioavailable than standard thiamine. It is fat-soluble (thiamine is water-soluble) which helps it more easily cross the blood-brain barrier.
The discovery of Sulbutiamine cured the Japanese population of a life-threatening disease. And it has since been tested and used throughout the world with much success.
Throughout this article I’ll refer to Sulbutiamine interchangeably with thiamine. Sulbutiamine is the stronger of the two so it’s affects are amplified compared to standard thiamine.
Thiamine is a coenzyme used by your body to metabolize food for energy. And to maintain proper heart, nerve and brain function.
Thiamine also helps digest and extract energy from food. It turns nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is the fuel created by your cell’s mitochondria.
And thiamine helps convert carbohydrates into glucose. The energy your body uses for your brain and nervous system.
One more thing about this miracle B-vitamin. Thiamine contributes to the development of myelin sheaths which wrap around axons to protect them from damage.
Sulbutiamine helps:
- Brain Optimization: Thiamine is critical for increasing focus, energy, and preventing memory loss. And can ward off inflammation. Healthy brain function is crucial for good decision making.
- Neurotransmitters: Thiamine is essential for producing the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh). ACh is used to relay messages between neurons in your brain. And is critical for cognition, learning and memory.
- Mood: Thiamine helps your body withstand stress. A lack of energy can contribute to poor mood and motivation. Thiamine can boost your mood, and defend against depression and anxiety.
What is Sulbutiamine? (thiamine derivatives)
Sulbutiamine is a synthetic version of Vitamin B1 (Thiamine). Japanese researchers synthesized Sulbutiamine by bonding two B1 molecules.
They developed Sulbutiamine in response to a country-wide health crisis. The Japanese population were severely thiamine-deficient from a rice-only diet. Large numbers of the population were suffering from Beriberi. A central nervous system disorder caused by a lack of thiamine.
Your body does not produce thiamine on its own. So you must get it from food including beef, brewer’s yeast, legumes (beans, lentils), milk, nuts, oats, oranges, pork, rice, seeds, wheat, whole-grain cereals, and yeast.
But thiamine has poor bioavailability. By synthesizing thiamine and producing Sulbutiamine you end up with a fat-soluble compound that is easily digested. And readily crosses the blood-brain barrier.
Sulbutiamine vs. Thiamine: What’s the Difference?
Sulbutiamine is a synthetic version of Vitamin B1 (Thiamine). It is two B1 molecules chemically bonded together.
Thiamine is water-soluble and does not easily cross the blood-brain barrier. Sulbutiamine is a fat-soluble compound that easily crosses the blood-brain barrier.
Sulbutiamine functions in the body just like thiamine. But because it’s more bioavailable it’s more effective than thiamine.
How does Sulbutiamine Work in the Brain?
Sulbutiamine boosts brain health and function in several ways. But two in particular stand out.
- Sulbutiamine is a fat-soluble molecule that crosses the blood-brain barrier more readily than thiamine. Once in your brain, it increases levels of thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP).
Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) is directly involved in the citric acid cycle in the brain.
This cycle breaks fatty acids, amino acids and monosaccharides into smaller molecules that produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) energy within your mitochondria. And provide the building blocks of the molecules needed to produce brain cells.
A deficiency of TPP can eventually show up as Wernicke encephalopathy and Korsakoff syndrome. In our society this syndrome is typically caused by chronic alcoholism. But it can also occur after obesity (bariatric) surgery, Crohn’s disease, anorexia and if you’re on kidney dialysis.
Symptoms of Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome include confusion, inability to form memories, loss of memories and muscle coordination, confabulation (making up stories) and vision changes. And can ultimately (and very rapidly) lead to coma and death.[i]
Less severe cases of thiamine deficiency include fatigue, weight loss, irritability and confusion.
- Sulbutiamine also contributes to the production of the enzyme PDH which is essential in making the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. And for the synthesis of myelin, which forms a sheath around the axons attached to neurons. Ensuring these neurons can conduct signals.[ii]
The citric acid cycle and enzyme α–KGDH play a role in maintaining optimal levels of the neurotransmitters glutamate, and gamma–aminobutyric acid (GABA).
When thiamine levels decrease, the activity of these enzymes are reduced.[iii]
How things go bad
We depend on our diet for thiamine. Very little thiamine is stored in your body. And depletion can occur within 14 days.
Thiamine deficiency can be caused by alcoholism, Alzheimer’s Disease, anemia, athletes who reduce food intake, cancer, clogged arteries, Crohn’s disease, diabetes, diarrhea and kidney disease. And even a poor diet.
↓ Low thiamine levels can slow creation of ATP
↓ Low thiamine levels can cause problems with memory, learning, recall and perception
↓ Acetylcholine levels decline
All of these changes can happen at any age. And are a product of the food we eat, what we drink, lifestyle habits, the air we breathe and more.
So Sulbutiamine can help age-related cognitive decline, as well as a student looking to do better in school. By boosting acetylcholine, dopamine and GABA in the brain. And increased brain energy by creating ATP within mitochondria. And building myelin sheaths that protect our axons.
Sulbutiamine benefits
Sulbutiamine is directly involved in the citric acid cycle that provides adenosine triphosphate (ATP) energy created within your mitochondria.
Sulbutiamine also plays a role in maintaining optimal levels of the neurotransmitters glutamate, and gamma–aminobutyric acid (GABA). And contributes to the production of the enzyme PDH which is essential in making the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
Sulbutiamine will boost cognition, memory and decision-making. And has very effective anxiolytic (anti-depressant) qualities.
How does Sulbutiamine feel?
Sulbutiamine is a fat-soluble form of thiamine which crosses the blood-brain barrier. It has been shown to improve glutamatergic, cholinergic, and dopaminergic neurological transmissions. It may also increase the density of D1 dopamine receptors.[iv]
Nootropics users report:
- Sulbutiamine as a study aid. On its own, Sulbutiamine seems to increase attention span for many neurohackers. And when combined with caffeine or any one of the racetams, many report being able to work effortlessly for hours on end. Study and work seems less stressful.
- Boost motivation. Sulbutiamine boosts motivation and many report gives them the drive they need for study or work.
- Increased focus. Sulbutiamine helps provide laser-like focus at work and school. Some report even with the most tedious of tasks. While staying in a very good mood.
- Sociability. Many users report being able to articulate thoughts, and improved speaking ability. Language and your vocabulary seem to flow effortlessly. Thoughts and ideas come with less effort.
- Improved mood. Personally, I’ve found Sulbutiamine to be more effective than any prescription antidepressant I’ve ever tried. And without the side effects.
You should be able to experience the effects of Sulbutiamine soon after you take it.
Sulbutiamine Clinical Research (thiamine deficiency)
Sulbutiamine Improves Mood
A study at the University of Wales Swansea in the UK worked with 120 young adult females. Study participants took either a placebo or 50 mg thiamine for 2 months. Mood, memory and reaction times were monitored before and after taking the tablets.
The results indicate that after 2 months of thiamine supplementation, the young females:
- Were more clear headed
- Felt more composed and energetic
- Reaction times improved
- Improved mood.[v]
Sulbutiamine for Chronic Fatigue
If you deal with chronic fatigue, Sulbutiamine may be a better option than another cup of coffee. Or a stimulant.
Researchers at the Hospital Saint-Antoine in Paris studied 326 patients. All suffering from chronic fatigue. Patients were given 400 mg or 600 mg of Sulbutiamine daily. Or a placebo in this double-blind, parallel-group study.
Patients were tested on the 7th and 28th days of the trial. Those that used 600 mg of Sulbutiamine had less fatigue.[vi]
Sulbutiamine Improves Memory
Poor memory is associated with low levels of choline activity in the brain. Choline is a precursor to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh). ACh transmission between neurons helps in memory formation.
Scientists decided to find out if Sulbutiamine could help boost choline uptake. They gave a group of mice Sulbutiamine for 10 days, and then tested their memory. The findings suggested Sulbutiamine improved memory formation. And it was due to an increase in choline activity in the brain.[vii]
Another study in France involved giving Sulbutiamine or a saline solution to rats for 9 weeks. The results of this study concluded Sulbutiamine provided better working and episodic memory.[viii]
Sulbutiamine Improves Athletic Performance
Many neurohackers use Sulbutiamine for a boost in physical energy. And it’s created some controversy in professional sports.
The Moscow Anti-Doping Center analyzed 16,000 blood samples in a Russian lab in 2009. They were looking for anabolic steroids in athletes.
They found that 100 samples contained Sulbutiamine. These samples were collected in-competition. Indicating that Sulbutiamine was intentionally administered for its “ergogenic and mild stimulating properties”.[ix]
Sulbutiamine Improves Erectile Dysfunction
One small study was conducted with 20 patients suffering from psychogenic erectile dysfunction. This type of ED is defined as the inability to achieve or maintain an erection because of psychological factors.
The men were given a prescription form of Sulbutiamine ‘Enerion’ for 30-days. 16 of the men showed significant improvement based on the international index of erectile function (IIEF).
3 of 6 men with arterial disorders in their penis showed that Sulbutiamine corrected the problem. The study concluded that erectile dysfunction can be effectively treated with Sulbutiamine.[x]
Sulbutiamine Dosage
Recommended Sulbutiamine dosage is 400 mg to 1,000 mg per day. Higher doses should be split with one dose in the morning, and the other early afternoon.
 Some neurohackers warn about dosing Sulbutiamine too late in the day. It’s mild ‘stimulant’ qualities could interfere with sleep.
Some neurohackers warn about dosing Sulbutiamine too late in the day. It’s mild ‘stimulant’ qualities could interfere with sleep.
If you’re just starting out with Sulbutiamine, I suggest starting with a low dose and see how your body reacts.
Tolerance can be a problem with Sulbutiamine. So when taking it for extended periods, you may find it beneficial to cycle on and off the supplement. For example, take Sulbutiamine for 5 days, and take 2 days off before your next dose.
Sulbutiamine powder tastes nasty. So you’d be advised to take it in capsule form. You can save on the cost of Sulbutiamine by making your own capsules.
And Sulbutiamine is fat-soluble so take it with a tablespoon of unrefined coconut or olive oil for better absorption.
Sulbutiamine Side Effects
Sulbutiamine is non-toxic. So is considered well-tolerated and safe.
Side effects are rare but can include skin rashes and eczema-like outbreaks at higher doses.
Sulbutiamine can also create mood swings. Particularly if you’re bipolar or are taking bipolar medication.
If you take Sulbutiamine late in the day you may find it interferes with sleep. Some find it has mild stimulant effects.
There are some reports that Sulbutiamine can be addictive. If you have addiction-like tendencies, you may want to be cautious about using this supplement. It does affect dopamine levels in the brain.
Where to buy Sulbutiamine
Sulbutiamine is sold in tablet, capsule and powder form. Tablets and capsules are usually 750 mg each.
It’s sold as a prescription medication in some countries under the brand names Arcalion, Enerion, Bisibuthiamine, and Youvitan.
In Dec. 2019, the FDA in the USA added Sulbutiamine to its “Dietary Supplement Ingredient Advisory List“. The FDA states that it, “does not necessarily indicate that the FDA has determined that the ingredient is unsafe; it means FDA is taking steps to further evaluate the ingredient.”
This means that you can no longer buy Sulbutiamine from vendors like Amazon or Bulk Supplements.
NOTE: This review contains affiliate links, and I will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on my links.
To buy Sulbutiamine, I highly recommend going here: Click for Science.bio- Sulbutiamine Powder (Science.bio went out of business Jan. 27, 2026) or Cosmic Nootropic – Sulbutiamine (Enerion®)
Nootropics Expert Recommendation
Sulbutiamine 400 mg to 1,000 mg per day
 I recommend using Sulbutiamine as a nootropic supplement.
I recommend using Sulbutiamine as a nootropic supplement.
Your body does not make Sulbutiamine on its own. So to get its benefits you must take it as a supplement.
Sulbutiamine is especially helpful for those suffering from depression. Experience shows it helps stop and reverse the symptoms associated with depression. Likely because this nootropic helps boost the activity of dopamine, serotonin, GABA and glutamate in the brain.
Personally, I’ve found Sulbutiamine to be more effective (and safer) than any prescription antidepressant I’ve ever tried.
Sulbutiamine is also particularly helpful to students and executives who want to boost cognition, learning and memory.
Sulbutiamine can produce a noticeable increase in mental clarity. And give you a significant energy boost physically and mentally. You’ll feel more awake and alert. Without the side effects you’d get from stimulants like caffeine.
Sulbutiamine also stacks very well with racetams like Piracetam and Aniracetam.
To buy Sulbutiamine, I highly recommend going here: Cosmic Nootropic – Sulbutiamine (Enerion®)








Join The Discussion - 201 comments
Judy
December 28, 2021
Hi David do you think this form of B1 would be suitable for my 9 yr old son. He has Autism and ADHD. He has already been taking B1- benfotiamine for some time.
After 3 months of trialling Ritalin we have decided to go back to more natural alternatives. The Ritalin made his anxiety and sleep worse plus it didn’t really work to calm his ADHD. The Dr wanted to increase the dose and add another med, that’s when we decided it wasn’t for us!
David Tomen
December 29, 2021
Judy, if he responded well to Benfotiamine he should do well with Sulbutiamine as well. The only difference is that Sulbutiamine can easily cross the blood-brain barrier and Benfotiamine can not.
But keep in mind that it is fat-soluble so for it to be effective it needs to be taken with a healthy fat or oil or a meal containing the same. Otherwise, it will not be digested and absorbed.
Rose
December 20, 2021
hi David,
Thank you for all the information that you share here, it’s fantastic!
Just wondering – Is taking Sulbutiamine as healthy as taking normal non synthetic B1? or does a person need to take both to keep vit B1 levels at a healthy level?
Basically can i just replace my intake of B1 with Sulbutiamine?
or to keep healthy do I also need to take B1, as well?
Also, Someone recommended – Benfotiamine
Is the same as Sulbutiamine, or do you know why Sulbutiamine would be better?
Thanks so much for your info, just bit confused over it all, cheers!
David Tomen
December 20, 2021
Rose, Sulbutiamine was invented by Japanese scientists to cure Beri-Beri which is a disease caused by severe thiamine deficiency.
Benfotiamine is better absorbed and used by your body than regular thiamine. But cannot cross the blood-brain barrier.
Sulbutiamine on the other hand works in your body AND brain. And if you are using Sulbutiamine there is no need to use regular thiamine. Keep in mind that Sulbutiamine is just two thiamine molecules bonded together. Which is fat-soluble and can easily cross into the brain.
Rose
March 17, 2022
hi David,
Quick question… does Sulbutiamine take the calcium out of your body?
A friend said that they used high levels of B1 and found they lost a lot of teeth and a doctor told them that they must use Calcium supplement when using high levels of B1.
Thoughts?
David Tomen
March 17, 2022
Rose, excess doses of anything is not a good idea. If you are going to use Sulbutiamine follow dosage recommendations and you should be fine.
Wesley
December 3, 2021
David, will you do a review on Bromantane?
David Tomen
December 4, 2021
Wesley, it is highly unlikely I’ll be doing a review of Bromantane anytime soon for a couple of reasons.
First, it is a prescription drug developed and still in use in Russia. It’s been banned by the World Anti-doping Agency for use by professional athletes.
And second, there is not nearly enough research in humans or animals to warrant a full review.
I class Bromantane as a “smart drug” and not a nootropic and I only review proven natural nootropic supplements here.
Flo Prock
September 20, 2021
Is sulbutiamine ever appropriate for people with bipolar disorder?
David Tomen
September 20, 2021
Flo, Sulbutiamine and Bipolar Disorder do not go well together. Esp. if you are using meds for Bipolar. And cannot say “yes” or “no” because it is unpredictable and tending towards the “no” end of the scale.
Flo
September 21, 2021
Thank you so much David for the quick reply!
I was just about to take a chance and order sulbutiamine, but fortunately you answered before I placed my order. Thanks for helping me stay safe..
I’m really disappointed that sulbutiamine isn’t a good option for me. Do you happen to know of a similar product to boost energy and motivation that is safe for bipolar? I get the sense that racetams may be risky as well.
My providers are unfamiliar with most of this stuff, so your feedback was very valuable and appreciated..
David Tomen
September 21, 2021
Flo, this is the way to boost energy: https://nootropicsexpert.com/best-energy-supplements-to-buy/
And this is how motivation works: https://nootropicsexpert.com/hacking-motivation-with-nootropics/
For the last one choose a couple of supplements that are not contrary to Bipolar Disorder.
GEORGIOS DRETAKIS
September 7, 2021
Hello
Thank you for your super work.
Can you tell me please which type of lipid-soluble thiamine is the best .
sulbutiamine / fursultiamine
Or any other
David Tomen
September 7, 2021
Georgios, I’ve been studying different forms of thiamine for over a decade and have concluded Sulbutiamine is the superior form of thiamine for use as a nootropic in most cases.
Chris
September 1, 2021
The combination of aniracetam and sulbutiame reminds of amphetamines (edgy and hopped-up sensation) but unfortunately it does nothing for focus and concentration. If fact it does the opposite, causing major brain fog and spacing out all the time. I am still trying to figure out if one or the other alone would be effective. I am leaning toward sulbutiame — testing still in progres.
David Tomen
September 2, 2021
Chris, interesting how these supplements can have a different reaction in each of us. I do not experience what you described.
Luke
August 30, 2021
Hi David,
I really enjoy your content, thank you! I see you don’t mention Allithiamine (TTFD) much in your articles, and I was wondering why you have a strong preference for Sulbutiamine? I’ve tried both and Sulbutiamine certainly has a more pronounced cognitive effect, but what do you think about the research regarding TTFD? From the research, it seems like this one has the most potential to get into cells, potentially detox heavy metals, and treat chronic conditions. It seems undeniable TTFD and Sulbutiamine are by far the best forms, but what is it about Sulbutiamine that edges out TTFD for you? If they both have the capacity to pass the cell membrane into the cell, why does Sulbutiamine have a more pronounced cognitive effect (which seems to indicate it is getting into the CNS to a greater degree)? Any insight you can provide here would be great! Even if it is just speculation.
David Tomen
August 30, 2021
Luke, Sulbutiamine has been around the longest as far as I know and I have 10 years of experience using it which is why I talk about it. There are plenty of studies showing how effective it is and that it easily crosses into the brain. And I figure why complicate things once you find something that works!
Malik
August 20, 2021
HELLO DAVID! What is causing tolerance to sulbutiamine? What can we add in our stack to avoid tolerance to sulbutiamine instead of cycle it . Thanks
David Tomen
August 20, 2021
Malik, there is nothing you can add to prevent tolerance to Sulbutiamine except to cycle it. There is no documented evidence of tolerance to this nootropic. Only anecdotal evidence. So why it happens is speculation. It may have something to do with down-regulating Kainite receptors which are glutamate receptors. But there is no proof that is the cause.