Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Noopept is a potent cognitive enhancer with various benefits for memory, learning, perception, and mood.
- It differs from traditional racetam compounds but still produces similar effects.
- It is up to 1000 times more potent than Piracetam and offers additional benefits, such as lower effective doses and influencing memory consolidation and retrieval.
- Noopept is considered safe within the recommended dosage range of 10 – 30 mg per day.
- In the USA, the best place to buy Noopept is Cosmic Nootropic – Noopept or Science.bio-Noopept Powder or Science.bio-Noopept Solution
Noopept (n-phenylacetyl-l-prolylglycine ethyl ester or GVS-111) is an ampakine nootropic similar in action to the racetam-class of compounds. Noopept is up to 1000-times more potent than the original racetam, Piracetam.
Noopept was patented by Russian-based pharmaceutical company JSC LEKKO Pharmaceuticals in 1996. Research shows Noopept has similar effects, but works differently than other nootropics in the racetam-family.
Noopept is not considered a true “racetam” because it doesn’t have a 2-oxo-pyrrolidine core.
Noopept does not appear in blood samples when taken as a supplement. Instead it elevates concentrations of cycloprolylglycine (CPG) in the brain.[i]
CPG is a dipeptide consisting of proline and glycine which acts as a modulator of acetylcholine transmission and AMPA receptor function.
Noopept is patented in both Russia and the USA. It is sold as a prescription drug in Russia, and other countries that were part of the Soviet Union. And as a supplement in the United States.
What does Noopept Do?
Neurohackers use Noopept to boost cognition, memory and learning. And to improve reflexes, perception, logical thinking and mood.
Noopept has also shown effectiveness in treating cognitive impairments related to conditions of vascular and traumatic origin, highlighting its therapeutic potential in managing cognitive deficits arising from organic brain diseases.
Noopept helps:
- Brain Optimization: Noopept increases Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF). Critical for neuroplasticity and Long-Term Potentiation. Brain health gets a boost along with long-term memory.
- Neuroprotection: Noopept prevents the release of excess glutamate in your brain. Glutamate is the brain’s primary excitatory neurotransmitter. When there’s a lack of oxygen in the brain, neurons can’t receive glutamate. This leads to toxic levels of glutamate within brain cells. And can result in neuron damage and death. Diminishing this neurotoxic overload with Noopept is potent neuroprotection.[ii]
- Brain Waves: Noopept boosts Alpha and Beta brain wave activity. You become calmer and more creative. It’s easier to go into a flow state. And you are prone to making innovative and resourceful decisions.
What is Noopept?
Noopept (nphenylacetyllprolylglycine ethyl ester or GVS-111) is often included in the racetam-family of nootropic compounds. But is not a true “racetam” because it does not have a 2-oxo-pyrrolidine nucleus.
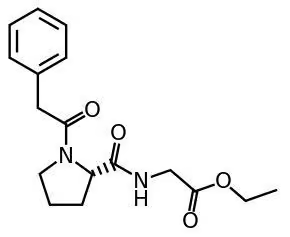
Noopept was developed in Russia where it is called Ноопепт or GVS-111. Russian-based pharmaceutical company JSC LEKKO Pharmaceuticals synthesized Noopept in 1996 based off the endogenous neuropeptide cycloprolylglycine (CPG).
Researchers in Moscow found Noopept mechanism of action similar to Piracetam in not only it’s nootropic effect, but also anxiolytic activity.[iii]
Noopept is a water-soluble ampakine nootropic. AMPA (α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic) refers to one of three glutamate receptors in your brain.[iv]
Noopept could also be considered a Cholinergic compound because it affects acetylcholine levels in the brain.
One of the newer synthetic nootropic compounds, Noopept is known as a cognitive enhancer. And is known for its anxiolytic, or anti-anxiety effects.
As a cognitive enhancer, a Noopept dose is considered to be up to 1000-times more potent than Piracetam. As an ampakine nootropic, it helps increase attention span, alertness and boosts all three levels of memory. Memory formation, retention and recall.
Ampakines tend to have a stimulant effect. But do not produce the same stimulant side effects as Ritalin or coffee from prolonged use.
What is Noopept Used For?
This novel cognitive enhancer, Noopept, is a synthetic nootropic known for enhancing cognitive function, offering neuroprotection, and boosting mental clarity. Although it shares structural similarities with the racetam family, like Piracetam, it is considered more potent and fast-acting. Here’s how it can be beneficial:
Neuroprotective Properties & Mitochondrial Apoptotic Pathway
Research indicates that Noopept acts as a neuroprotective agent by influencing the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway (mitochondrial function), of which is crucial for determining whether nerve cells survive or undergo programmed cell death (apoptosis).
This function is vital for safeguarding brain tissues against oxidative damage and the toxic buildup of substances classified as harmful such as Amyloid-β.
Studies suggest that Noopept can significantly reduce the percentage of late apoptotic cells in neuronal cells, further proving its neuroprotective effects.
One significant threat to nerve cells is amyloid beta exposure, linked to diseases like Alzheimer’s.
Studies suggest that Noopept can significantly attenuate tau hyperphosphorylation and reduce late failure in neuronal cells, promoting synaptic plasticity.
This makes it a promising intervention for mild cognitive disorders or organic brain diseases such as Alzheimer’s.
Noopept as a Cognitive Enhancer & Psychoactive Substance
Noopept is recognized as a novel cognitive enhancer due to its ability to improve memory, learning, and focus, without the jittery side effects typical of other psychoactive substances.
It enhances mental energy and positively affects the central nervous system by supporting nerve cell regeneration, boosting neurotransmitter activity, and strengthening brain tissue resilience.
With its neuroprotective effects, Noopept can benefit those with cognitive deficiencies and also serve as a standard cognition enhancer for healthy individuals seeking to enhance their cognitive function.
It supports intracellular calcium homeostasis and reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines accumulation, further protecting against common pathogenic pathways in brain health.
Noopept vs. Piracetam: What’s the Difference?
Russian-based pharmaceutical company JSC LEKKO Pharmaceuticals developed Noopept in the late 1996 as a peptide analogue of the original nootropic Piracetam.[v]
Noopept and Piracetam are both water-soluble. And both Noopept and Piracetam are cognitive enhancers. Both have neuroprotective and anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) qualities.[vi] Both racetams are able to improve learning and memory. And both are able to repair brain damage.
But Noopept has additional benefits not shared with Piracetam. First, the effective dose of Noopept compared to Piracetam is 1,000-times lower. A typical dose of Noopept is 10 – 30 mg while Piracetam is often dosed up to 3 or 4,000 mg.
Second, Piracetam facilitates only the early stages of the memory process. On the other hand, Noopept influences memory consolidation AND retrieval steps as well. But if someone claims “is Noopept a stimulant” it’s simply not true.
So Noopept helps you develop the memory, retain the memory, and then recall what you have stored in memory.[vii]
Noopept also has additional selective anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) action. Researchers believe this is due in part to Noopept’s antioxidant effect, anti-inflammatory action, and the ability to prevent the neurotoxic effect of too much calcium and glutamate.
How does Noopept work in the Brain?
Noopept boosts brain health and function in several ways. But two in particular stand out.
AMPA & NMDA Neuroreceptors
- Noopept modulates AMPA and NMDA receptors and acetylcholine (ACh) transmission. Noopept boosts the level of cycloprolylglycine (CPG) in the brain. CPG is a dipeptide consisting of proline and glycine which acts as a modulator of acetylcholine transmission, and AMPA and NMDA receptors.
When brain cells are starved of oxygen, glutamate which is your brain’s primary excitatory neurotransmitter, does not work efficiently with neuroreceptors. The result can be a toxic buildup of glutamate within brain cells. Causing neuron damage and ultimately, neuron death.
Noopept modulates neuroreceptor function keeping glutamate transmission at normal levels. Protecting neurons and other brain cells from glutamate damage.
Noopept has also been shown to modulate acetylcholine flow in your brain. Restoring the harmony of glutamate and acetylcholine function not only protects your brain from damage. It can boost cognition, memory, learning, recall, mood and relieve anxiety.
Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF)
- Noopept increases Nerve Growth Factor (NGF), Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) and mRNA. NGF and BDNF are directly related to neuroplasticity. This ability to repair and even grow new brain cells can have profound implications. Particularly with someone with neurodegenerative brain damage like Parkinson’s or Alzheimer’s. And even affecting Long-Term Potentiation needed for long-term memory development.
mRNA affects the expression of genes and intracellular communication in brain cells. This ongoing brain signaling and gene expression within brain cells is required for healthy cognition.
One study conducted in Moscow showed long-term use of Noopept boosted NGF, BDNF and mRNA. The animal subjects in this study showed no sign of tolerance. And long-term use of Noopept even potentiated the neurotrophic effect.[viii]
How things go bad – Glutamate in the Central Nervous System
Glutamate is an excitatory relative of GABA. While GABA has a calming effect, glutamate stimulates. Glutamate is the most common neurotransmitter in the central nervous system.
But glutamate can be toxic to neurons. And too much of it in your brain can kill brain cells. Lou Gehrig’s Disease for example, is caused by excess glutamate.
But glutamate is a pivotal neurotransmitter in the brain. It links the brain circuits involved in memory, learning and perception.
↑ Too much glutamate can kill neurons
↓ Too little glutamate can cause problems with memory, learning and perception
↓ Acetylcholine levels decline
↓ Nerve Growth Factor declines
↓ Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor declines
All of these changes can happen at any age. And are a product of the food we eat, what we drink, lifestyle habits, the air we breathe and more.
So Noopept can help for age-related cognitive decline, as well as a student looking to do better in school. By boosting NGF, BDNF and acetylcholine, and controlling glutamate in the brain.
Noopept benefits
Noopept modulates AMPA and NMDA receptors. AMPA receptors are associated with how glutamate and calcium is used in your brain. As a neuroprotective agent Noopept, it’s more of a neuroprotective role.
Similar to the AMPA receptor, the NMDA receptor is also associated with glutamate and calcium use in your brain. They work together to modulate how neurons use glutamate.
Noopept modulates levels of glutamate within and between neurons. It prevents glutamate toxicity, and influences Long-Term Potentiation (LTP). LTP is associated with neuroplasticity that allows long-term memories to form.
There is clinical evidence that Noopept boosts communication and neuron signaling. By boosting Alpha and Beta brain wave activity. You become calmer and more creative. It’s easier to go into a flow state. And you are prone to making innovative and resourceful decisions.
Noopept produces an anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) effect. It stimulates dopamine receptors (D2 and D3) and acetylcholine nicotinic receptors. And Noopept also seems to modulate some serotonin receptors. All contributing to a better mood and less anxiety.
Noopept has been shown in the lab to boost Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF). NGF and BDNF are both involved in neuroplasticity, and the repair and replacement of damaged brain cells. Resulting in overall better brain health, memory and cognition.[ix]
Noopept is water-soluble and quickly enters your brain after you take it. Once in your brain, it boosts signal transmission, and protects neurons.
How does Noopept feel?
Nootropics users report:
- Noopept as a study aid. On its own, Noopept increases focus and attention for many neurohackers. Mental arithmetic and grasping difficult concepts is easier.
- Increased verbal fluidity. Your conversation skills could increase with Noopept. Vocabulary comes easier. Being able to focus contributes to a more balanced dialogue. Neurohackers report being more outgoing, friendly and less self-conscious.
- Improved mood. With Noopept you may find yourself better able to deal with stressful situations and work issues that normally get you down. Once you get past the first few weeks of unpleasant memories related to PTSD you may find overwhelming emotions will subside. You could feel detached in a pleasant way from painful memories.
- Music appreciation. Many users report increased pleasure when listening to music while using Noopept. For some it takes music to a different plane. Distinguishing between instruments in sound tracks is easier. As a whole, music sounds better.
- Long-term memory. Noopept affects NGF and BDNF which affects long-term potentiation. Some neurohackers report memories long forgotten suddenly spring up. Which could be good or bad I suppose depending on the memory. But reports say memories are clear. And if they’re unpleasant there is an emotional detachment shielding from unpleasant feelings.
You should be able to experience the effects of Noopept soon after you take it. It’s water-soluble and enters your cells quickly especially if you take it sublingually.
A word of caution however; don’t go over the recommended 10 – 30 mg per day dose! You will not experience any added benefit, and could bring on unwanted side effects.
There is some debate on the water-solubility of Noopept. It’s not truly fat-soluble but it certainly doesn’t hurt to use a quality “good fat” when taking your Noopept dose.
Noopept Clinical Research
Noopept increases Nerve Growth Factor & BDNF
A study published by the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences in Moscow shows that Noopept stimulates Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF).
In this study, researchers studied the effect of single and long-term treatment (28 days) of Noopept. They found that one-time treatment boosted mRNA in the cerebral cortex of rats. mRNA is a molecule in brain cells that carries codes from DNA where they specify the amino acid sequence of proteins.
And long-term treatment of Noopept increased Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF). The researchers speculated that this sequence of events in the brain plays a role in the restoration of neurons.
Improving neurotrophic synthesis in the hippocampus boosts cognitive function. Particularly consolidation and delayed memory retrieval.
The research team concluded that Noopept “holds much promise to prevent the development of Alzheimer’s disease in patients with mild cognitive impairment”.[x]
Noopept boosts Brain Waves
Researchers in Moscow studied the effects of injecting Noopept in rats to see how it would affect brain waves.
The team found that Noopept increased Alpha and Beta brain wave activity throughout the brain.
You experience Alpha waves as you become more relaxed. Alpha waves are associated with super-learning, flow state and joy. Beta waves are associated with concentration, alertness and cognition.
The researchers observed that NMDA receptors were involved with a single injection of Noopept. While AMPA receptors were activated after longer-term use of Noopept.[xi]
NMDA receptors are associated with Long-Term Potentiation (long-term memory) and neuroplasticity. AMPA receptors are associated with increased brain signaling activity. Boosting cognition and memory.
Noopept improves memory
Noopept is known within the nootropic community to enhance cognitive function and memory. And dozens of studies support this claim of better memory when using Noopept.
One study done at the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences in Moscow conducted animal studies, experimenting with Noopept on rats. The animals were trained in passive avoidance response.
The animal’s ability to both form a memory and retain a memory was impaired. But once the rats received a dose of Noopept, they were able to retain a memory and retrieve that memory later.
In other words, their cognitive functions improved. Noopept normalized learning capacity in animals that had damage done to their cerebral cortex. And promoted training ability in rats who started with a hereditary learning deficit.
The researchers noted that “Noopept improves all three stages of memory”. And was most pronounced in those with impaired memory function.[xii]
Another study, again done with rats noted that Noopept stimulated learning after just a single administration. And repeated administration actually increased the number of successful learners among the animals who failed the initial training.[xiii]
Noopept Dose
You’ll find recommended Noopept doses ranging from 10 – 30 mg per day.
Noopept is very bioavailable and easily crosses the blood-brain barrier.[xiv]
Noopept is sold in tablet, capsule and powder form. Tablets and capsules are usually 10 mg each.
Noopept is primarily water-soluble nootropic, but won’t easily dissolve in water or juice. So it may help if you take it with a meal containing healthy fats. Or with a tablespoon of extra virgin, expeller cold-pressed coconut or olive oil. Or other similar healthy fat to ensure quick absorption.
For even quicker absorption you can use Noopept sublingually. Let the tablet or powder dissolve under your tongue so it can go straight into your bloodstream, and into your brain. Bypassing your digestive system completely.
Noopept Side Effects
Is Noopept dangerous or is it safe to use? Noopept is a synthetic nootropic and consider non-toxic. So is considered well-tolerated and safe. As long as you stay within the recommended dosage.
Side effects are rare but can include fatigue, headaches, insomnia or stomach upset. Side effects are often a result of unusually high doses of the nootropic.
Recent research has found that Noopept promotes the level of the Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF1α) protein. This action helps increase oxygen supply to areas where oxygen levels are low. But it also means that increasing the oxygen supply to tumor cells helps those tumors to proliferate. So, if you have cancer of any kind you should not use Noopept.
Headaches from using Noopept typically happen when you forget to combine it with a good choline supplement. Headaches are often a symptom of a choline deficit in your brain.
Where to buy Noopept
Noopept is sold in tablet, capsule and powder form. Tablets and capsules are usually 10 mg each.
In the USA, you can buy Noopept from Click for Cosmic Nootropic – Noopept
And you can also get Noopept powder or liquid from Science.bio, who have just opened their store again. Click for Science.bio – Noopept Powder or Click for Science.bio – Noopept Solution who sell Noopept as a “research” compound. It is sold to be used in an academic laboratory research setting. They go on to state “nothing we sell is intended for nor is it manufactured for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes in humans.”
In Russia and some other Eastern European countries, Noopept is a prescription drug.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does Noopept make you feel?
Students who use Noopept as a study aid say it helps them with focus and attention. Mental arithmetic and grasping difficult concepts is easier. Many say Noopept helps with verbal fluidity. They report being more outgoing, friendly and less self-conscious.
With Noopept you may find yourself better able to deal with stressful situations and work issues that normally get you down. Many users report increased pleasure when listening to music while using Noopept. And Noopept seems to help reconnect brain circuits so it is easier to remember long-lost memories. And I personally find that when I use Noopept, I’m more productive.
Does Noopept actually work?
Noopept really does work. See the section above on How does Noopept feel? And see what real users say about their experience with Noopept for studying, listening to music, improving verbal fluidity, and putting them in a better mood.
Is Noopept legal in America?
Noopept has not been approved by the FDA in the USA as a dietary supplement. So supplement bottles will often say the contains contain a “research compound”. It is NOT illegal to buy or own Noopept in America.
Is Noopept a banned substance?
Noopept is not a banned substance in America. Neither has it been approved by the FDA as a dietary supplement. Noopept has not been “scheduled” in Australia, is available OTC in Brazil, but Noopept may be held up in customs in Canada, and so on. For other countries around the world, see my article Are Nootropics Legal in My Country?
Nootropics Expert Recommendation
Noopept 10 – 30 mg per day
 I recommend using Noopept as a nootropic supplement.
I recommend using Noopept as a nootropic supplement.
Your body does not make Noopept on its own. So to get its benefits you must take it as a supplement.
Noopept is especially helpful for those looking to boost cognition, memory and recall. This nootropic helps boost the activity of acetylcholine in your brain. It modulates glutamate receptors which normalizes optimal neurotransmitter function. And increases Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) which helps the neuroplasticity needed for Long-Term Potentiation.
Noopept is also particularly useful to students and executives who want to boost cognition, learning and memory. My experience using Noopept shows it helps boost study scores, workflow, learning and memory.
Noopept also helps improve verbal fluidity and sociability. Words seem to come easily, and vocabulary you didn’t know you had access to come into play.
Music sounds richer and fuller, and your listening experience enters a new level of music appreciation.
You should stack Noopept with a good choline supplement like Alpha GPC or CDP-Choline. It helps boost neural acetylcholine, so demands the presence of more choline in your brain.
You should not exceed Noopept doses of more than 30 mg per day. This nootropic supplement is highly bioavailable and passes through the blood-brain barrier quite easily. Start with 10 mg and see how you respond.
In the USA, you can buy Noopept from Click for Cosmic Nootropic – Noopept
And you can also get Noopept powder or liquid from Science.bio, who have just opened their store again. Click for Science.bio – Noopept Powder or Click for Science.bio – Noopept Solution







Join The Discussion - 216 comments
Dean
November 27, 2019
Hi,
Today arrived my Noopept 30mg and Alpha GPC 150mg.
I already have and use in morning Piracetam (powder) about 2.5-3.5g, Choline L-bitartrate (powder) about 700mg and L-Theanine 200mg (cap.).
My question is how to combine now with Noopept and Alpha GPC?
I think to use maybe about 2g Piracetam and 700mg Choline in the morning and later in the day (after several hours) to take 1 Noopept and 1 Alpha GPC 150mg capsules?
What do you think?
Before I go to sleep I swallow one Melatonine cap. 300mgc
p.s. I am about 94Kg in the middle 30s and I’m not sure do I have some Nootropics to take in a bigger dosage, are those dosages for average body size (male about 75-85) or it doesn’t matter.
David Tomen
November 27, 2019
Dean, dosages sound about right but Noopept is maximum dose of 30 mg per day. Better if you did three doses of 10 mg each morning, noon and mid-afternoon. But if not then your plane of Piracetam in the morning and Noopept later should work.
Keep in mind that Alpha GPC and Choline Bitartrate are both used for the synthesis of acetylcholine. You just need a third of the amount of Alpha GPC compared to Choline Bitartrate because the latter does not easily cross the blood-brain barrier.
You may need a higher dose of Choline Bitartrate with 2 g of Piracetam. And that amount of Noopept will likely require at least 300 mg Alpha GPC.
Dean
November 28, 2019
I ordered of 30mg per cap. Is it ok to use in the morning 1 cap (30mg) of Noopept + 300 mg Alpha GPC and about 5 pm to take Piracetam with Choline? Because both are in powder and I don’t plan to bring on work. That is the reason why I take them in the morning.
How much Choline to take than? I reduce Piracetam on about 2g only because now I have Noopept. Do you think that is ok?
David Tomen
November 29, 2019
Dean, unless you work all night I’d hesitate to use Piracetam at 5 PM. It’s not a stimulant but it will likely cause insomnia.
As for “how much choline” you’ll need to experiment. If you don’t use enough you’ll get a racetam-headache. And if you use too much you’ll likely get sleepy. Trial and error until you find what works best for you.
Dean
November 29, 2019
Thanks a lot!
Bobby
November 25, 2019
I am currently taking Mind Lab Pro and 250MG of Uridine. I want to add 10mg of Noopept to my daily dosage. Is this okay?
David Tomen
November 26, 2019
Bobby, you sure can but it’s best to add 300 mg of Alpha GPC or CDP Choline which helps both Uridine and Noopept work better.
Mike
October 12, 2019
Hi David, I took 30 mg of Noopepet along with 250mg CDP-Choline, It worked wonders for me the first couple of days and experienced all the benefits, but on the 3rd day, it just gave me severe brain fog and made unmotivated to do anything. I tried to take half of the capsule and it gave less brain fog. My stack contains 1g of DHA, 200mg of L-theanine, 350mg of NALT and 500mg of L-tryptophan.
What causes that in your opinion?
David Tomen
October 14, 2019
Mike, sounds like your Noopept dosage was too high. The lower end of the recommended dosage is only 10 mg. Try that and if it still causes side effects then it’s a sign this nootropic is not for you.
Leo, Denmark
September 26, 2019
Hi David,
I have well-controlled hypertension and I would like to try Noopept. I found out that Noopept can raise blood pressure. On the other hand, I was thinking to supplement it with Alpha GPC. Now, as I understand it, Alpha GPC is known to lower blood pressure. So, do you think Noopept + Alpha GPC together won’t affect blood pressure drastically?
This is my current stack:
10 mg stabilized NADH
2 gr. Fish Oil
25 mg DHEA
Vitamin B Complex with Magnesium and Vitamin C
30 mcg Vitamin D
And now I would like to add:
10 mg Noopept
150 mg Alpha GPC
I would like to hear your expert opinion on this.
Thank you in advance.
Best regards,
Leo
David Tomen
September 27, 2019
Leo, you should be OK with Noopept dosages at the low end with Alpha GPC. Try it and see how it works. If it does, I think you’ll love this nootropic.
Eric R Ellquist
September 25, 2019
Hi David, thanks again for all the information, a life saver and a quality of life enhancer. I have a couple of questions: Is it OK to take Noopept with Oxyracetam, I found that I can only take the Oxy once a day as I get too much of a stimulative reaction too it. Once I finish the amount that I purchased, I intend to go back to the Aniracetam.
Secondarily, I take five grams of l-glutamine daily along with five grams of creatine monohydrate as part of my workout stack. As glutamate is synthesized from glutamine, I wonder if the problems with anxiety might be increased by taking this supplement. At 68 years of age, the weight training is as much a part of my quality of life stack as the nootropics I take, and glutamine is a part of that. My mom had age related dementia,at a relatively young age and while I don’t know if it may be hereditary, I am unwilling to take the chance. I also take alpha GPC, bacopa, lithium orotate (5mg twice daily), magnesium glycinate, l-theanine, one gram of L-lysine, ALA, and five mg of melatonin (before bed) daily.
Much of what I use is due to the apparently age related cognitive issues I am experiencing.
David Tomen
September 27, 2019
Eric, you can use Noopept and Oxiracetam but you may need to increase your Alpha GPC dosage.
I know that NAC helps regulate glutamate: https://nootropicsexpert.com/n-acetyl-l-cysteine/. There may be a couple of others but you’d need to search for “glutamate” and see what else turns up.
Here’s a post of preventing age-related cognitive decline which may give you some other ideas to try, or at least help refine your strategy: https://nootropicsexpert.com/best-nootropics-for-the-aging-brain/
Brigitte
September 10, 2019
Hi David, Thanks for sharing your expertise on this fantastic site, I have been on it for 2 days!
Would you mind explaining why you use Aniracetam if you think Noopept is so much better? Also, do you use everything written on your personal list on a daily basis? That seems huuuge! 🙂
I have complex PTSD, the facets of which translate in high anxiety, hypervigilance, ADD, social phobia, OPCD, random focus, poor memory and depression, and your page is a mine of healing possibilities for me, but it’s bit hard to pick what to start with.
I already use a few things for anxiety on a regular basis, ashwagandha, rhodiola and vit B complex and occasionally bacopa, and I keep thinking I take too many things and my body will just adapt to them and stop working… That said, it is better that it was although I am still anxious, but by far doesn’t cover everything and surely not the memory problem, which I believe is a focus problem, which I believe is an anxiety problem – I have an imprecise recollection of things, for instance I know I have seen or heard about something, I know what it is for, but I can’t remember where I have seen it or its name. I have a hard time with names or nouns and as I live in a foreign country, my vocabulary hardly increases at all and I have a pathetic accent. What would you advise? Thanks!
David Tomen
September 11, 2019
Brigitte, Aniracetam and Noopept have two completely different mechanisms of action and each provides unique benefits. Compare what you’ve read in this review to Aniracetam here: https://nootropicsexpert.com/aniracetam/. Also compare the sections on “How does it feel?”
I take everything on the What I Take list everyday and have for many years. I used to experience all of the symptoms you have described. But those symptoms have long since disappeared. But the thing is it took everything in my stack to achieve this and using them consistently.
Nootropics, if they are dosed correctly and used as recommended do not lose their effectiveness. You body “heals” rather than “adapts” to them.
Brigitte
September 30, 2020
Hi David, sorry I haven’t answered before, I just discover your reply, I never got the notification email it seems. My stack has dramatically increased thanks to you fantastic website. I have just started my own stack of CILTEP and am quite happy with it, although it does take a bit of fine tuning for the quantities. Right now I only take it every second day. I am only getting in the racetams now after months of not knowing where to start. And I am ordering Polygala tenuifolia, which is said to be as effective in ADD as it may support neuroplasticity and help promote spatial awareness and organization. Apparently it is believed to increases both levels of BDNF and NGF and may also help promote sleep quality so I think I should take Noopept in the morning and Polygala in the afternoon, does it make sense? Do you have any feedback on Polygala? Thanks!
David Tomen
October 1, 2020
Brigitte, I have not done the research on Polygala so can’t comment either way. But I’m an old-fashioned kind of neurohacker and would use Lion’s Mane if I wanted to boost Nerve Growth Factor and BDNF. So if you are using Polygala to boost BDNF and NGF it doesn’t matter when you take it. You just need to do it consistently.
Noopept should be used morning and noon. With a choline supplement like Alpha GPC or CDP-Choline.
Jason
September 5, 2019
Well, just as I took several CBD gummies and 15 mg of noopepet 300 mg of alpha GPC. I read the post that said you shouldn’t mix CBD and noopept so that’s good. I guess I’ll just update you on if anything bad happens or not.
Alot of people recommend using gingko with alpha gpc since Gingko reducing the reuptake of the acetylcholine from what I remember? I could be wrong on this.
Is noopept + alpha GPC + gingko a good long term stack?
Also do we really think CBD could be dangerous mixed or just because it does not have as much research, it is not recommended?
David Tomen
September 5, 2019
Jason, Ginkgo acts as a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) which boost dopamine. And not acetylcholine. Noopept on the other had modulates acetylcholine transmission and is more effective when stacked with Alpha GPC.
CBD Oil has a completely different mechanism of action. It enhances serotonin and glutamate signaling via 5-HT1A receptors. It enhances GABA transmission and increases levels of anandamide. CBD increases the activity of the native endocannabinoid system by increasing cannabinoid receptor density.
I see no problem with stacking Noopept + Alpha GPC + Ginkgo longterm.
Steven
April 29, 2021
Hi, sorry this is several years after the fact. But I take CBD on a daily basis, and I’m about to start taking Noopept. I gather from Jason’s post that there’s information about not combining the two, but a search of this site hasn’t turned up any leads.
Is there a reason these two nootropics aren’t supposed to be mixed? What happens if you do?
David Tomen
April 30, 2021
Steven, there is no issue about using CBD Oil and Noopept. It is not a problem.
VICTOR
August 8, 2019
Hello,
I bought noopept 10 mg , but i dont exactly how to take , in the mornings before a meal or after a meal ? and also in the afternoon before lunch or after lunch ?
Thanks
David Tomen
August 8, 2019
Victor, you can take Noopept with food. But for the best absorption your meal needs to have plenty of healthy fats. Or, just take your Noopept dose with a tablespoon of unrefined coconut oil. And a good choline supplement; Alpha GPC or CDP-Choline.